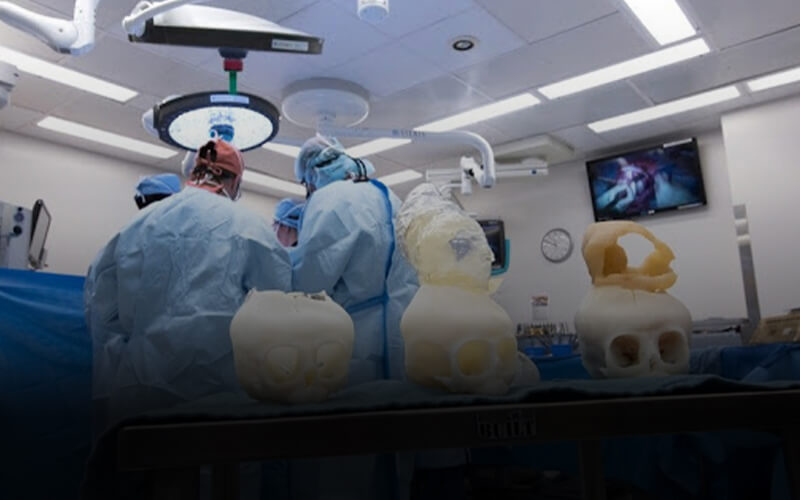
Industrial 3D Printing Machine
Dreambot3d industrial 3D printing machine is used for printing all sizes of 3D objects across different industries. The industrial 3D printing machine by Dreambot3d prints at a fast speed and has excellent printing precision.
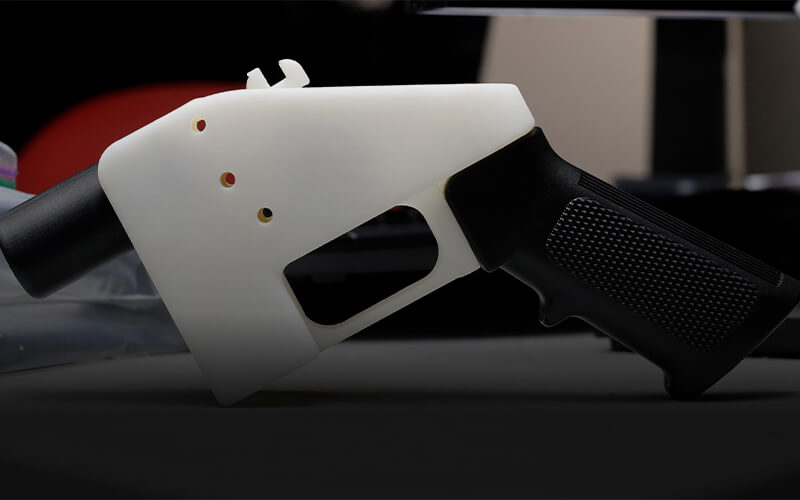
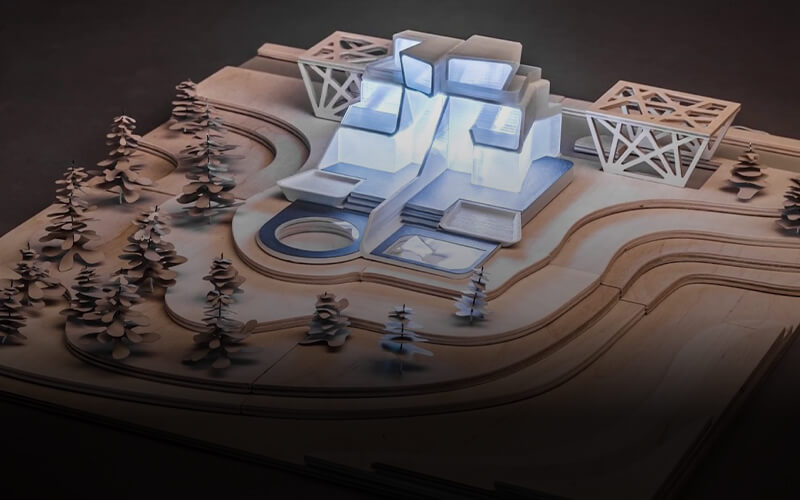
The industrial 3D printer is used for printing anime objects, jewellery moulds, architectural models, gun models, etc.
Contact Us
Industrial 3D Printing Machine
- The industrial 3D printing machine prints at a high speed and produce quality parts with precision.
- Dreambot3d printer has a user-friendly interface and software that prints numerous parts at the same time.
- The standard and quality certification institutions certify our products due to the original printers we produce.
Dreambot3D Industrial 3D Printing Machines list
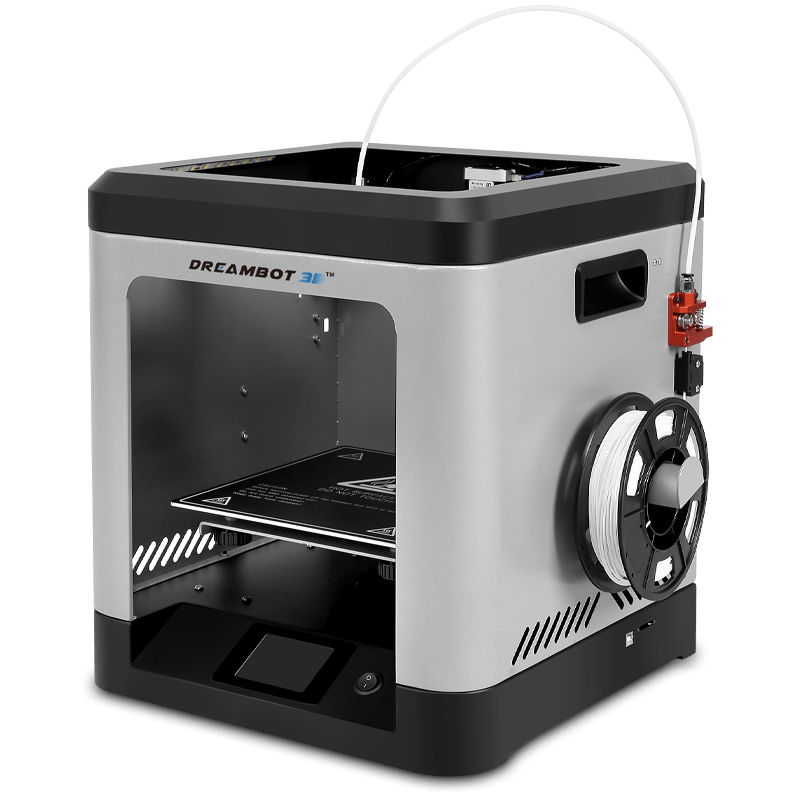

The L-200 3D printer prints 200*200*200mm sized 3D objects. The fast speed of printing is between 20-150mm.
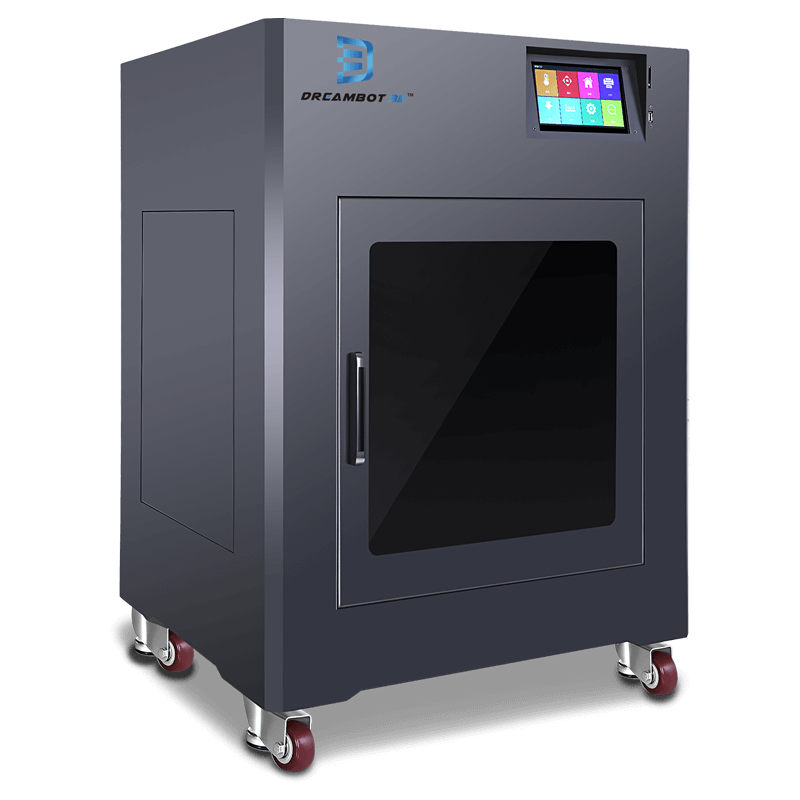

The L-300 3D printer has a build volume of 300*300*400mm. It has a positioning accuracy of 0.0011*0.0011*0.00125mm.
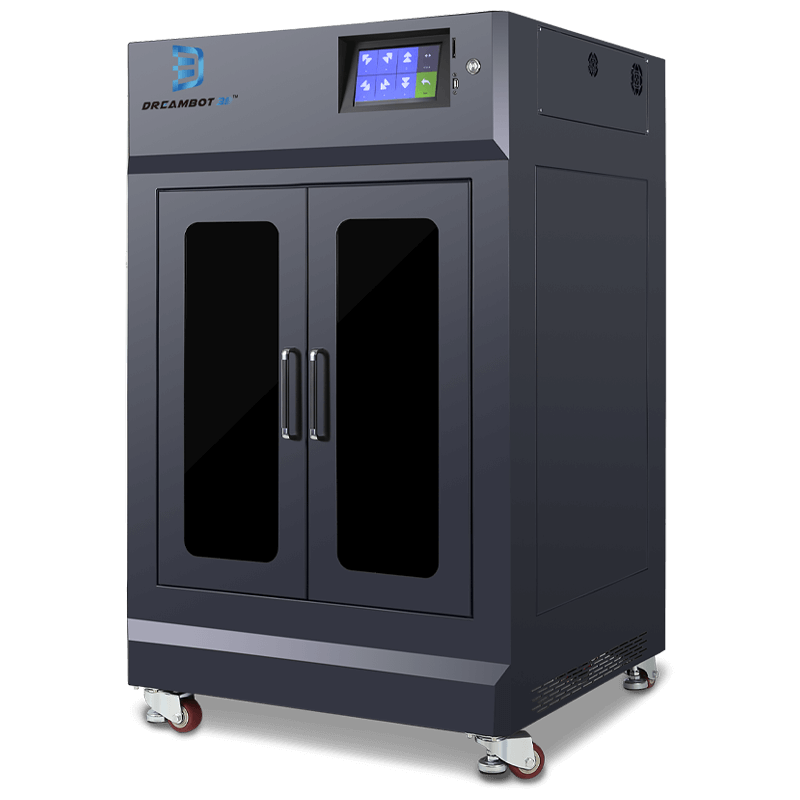

The L-400 3D Printer has a printing volume of 400*400*500mm with a printing speed of 20-150mm.
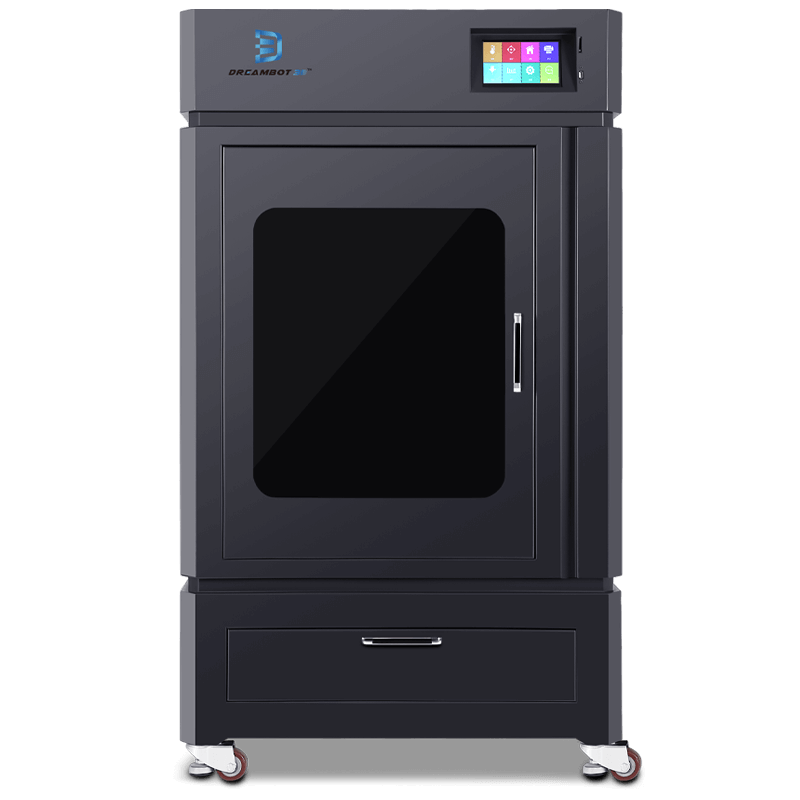

The L-500 3D printer prints objects at a size of 500*500*800mm. The nozzle diameter is between 0.2 to 0.8mm.
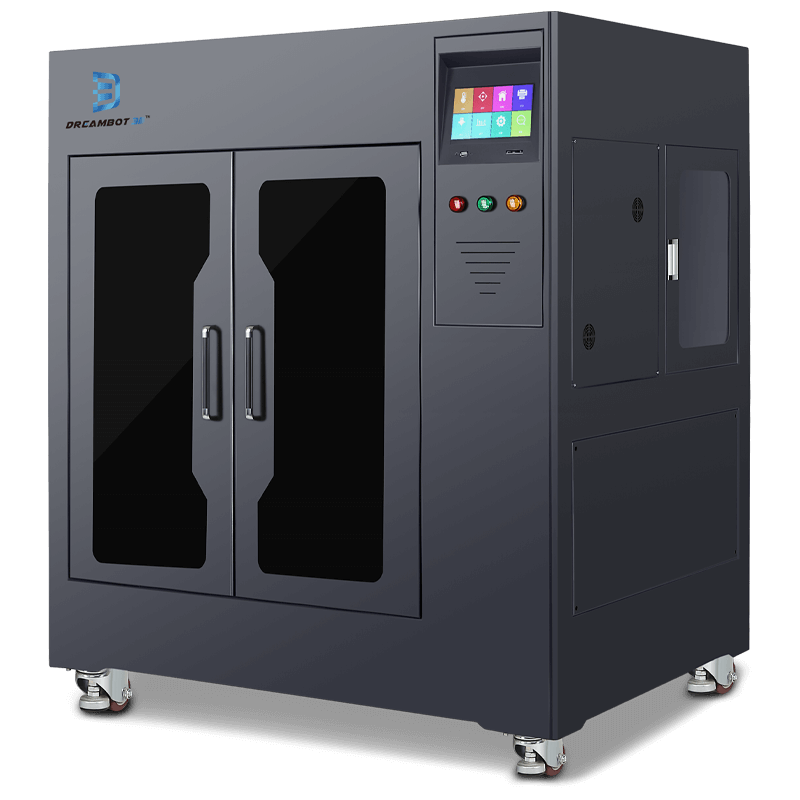

The L-600 3D printer prints at the size of 600*600*800mm. The speed of printing is 20-150mm.
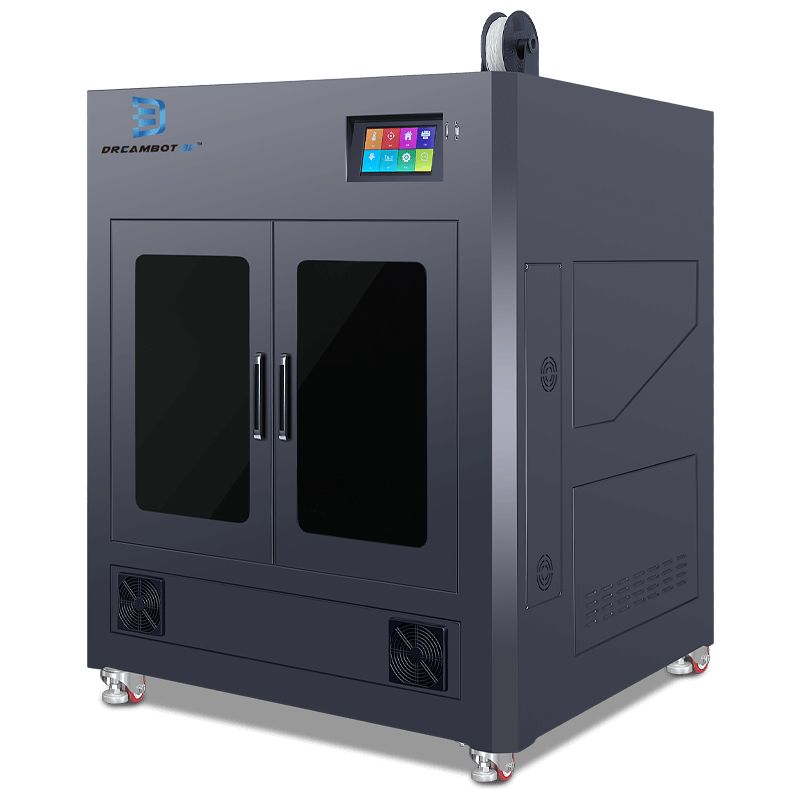
The L-800 3D printer has a printing volume of 800*800*800mm. Each printed item has a layer thickness of 0.05-0.3mm
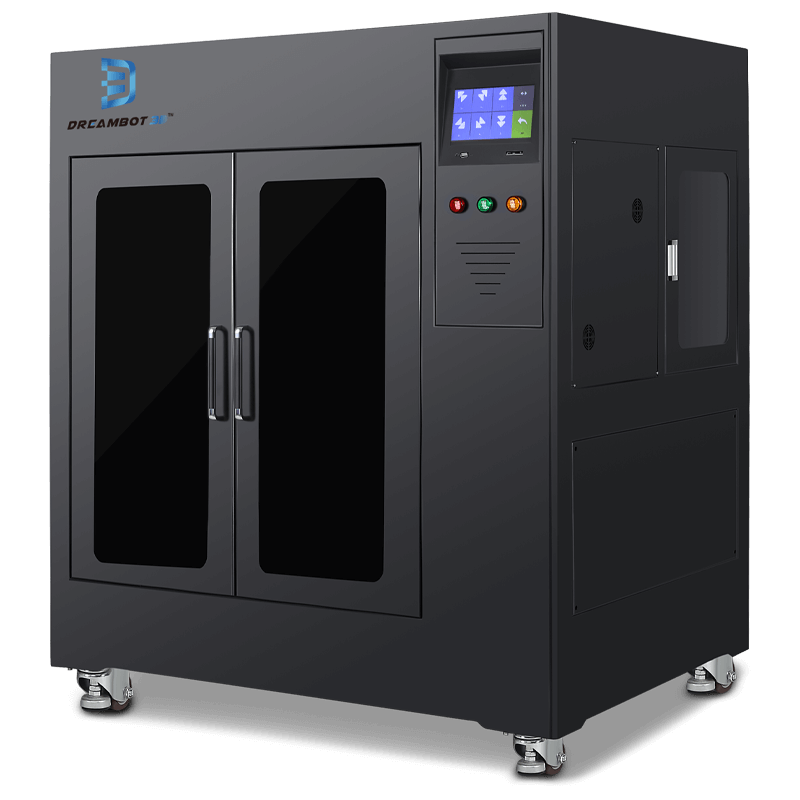

The L-1000 3D printer prints objects at the size of 1000*1000*1000. The consumable diameter is 1.75mm.
Application of Industrial 3D Printing Machine
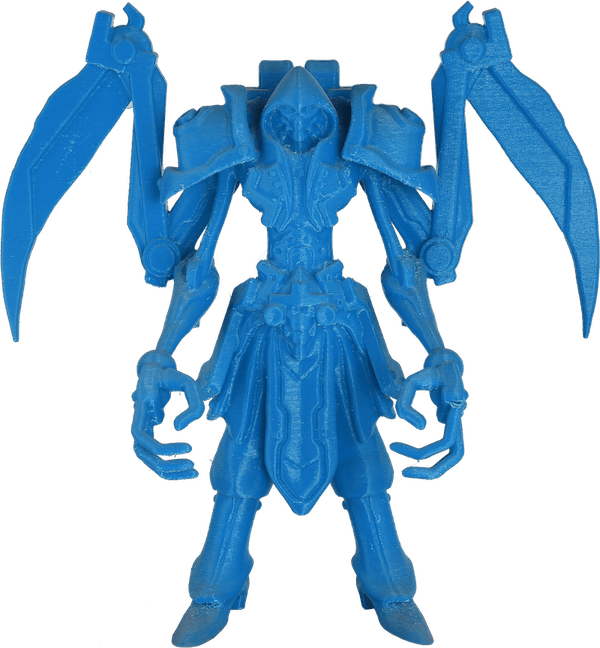

Test your part
We provide sample testing service, allowing you to check the working quality of our 3D printer before placing an order
6 points why choose us

Automatic resume printing
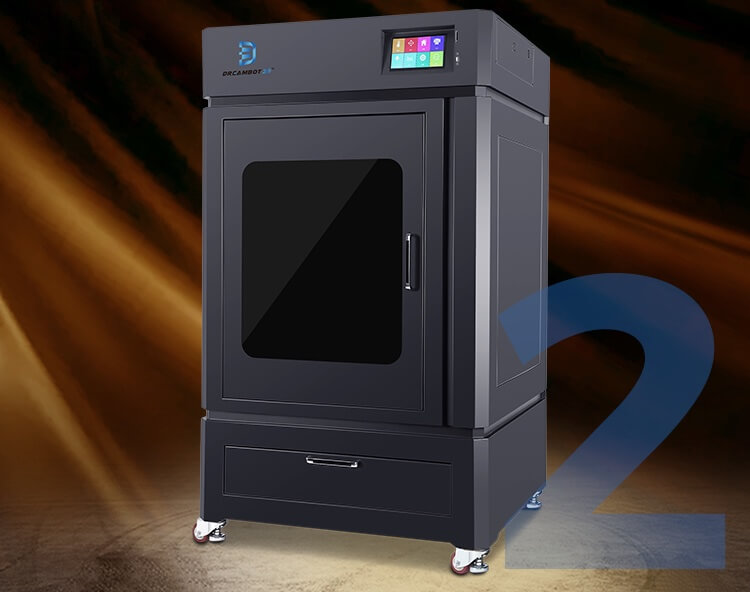

Full enclose stable frame
The whole machine case is thickened by CNC cutting, with accurate hole position, better assembly stability, and higher positioning accuracy of printer operation.
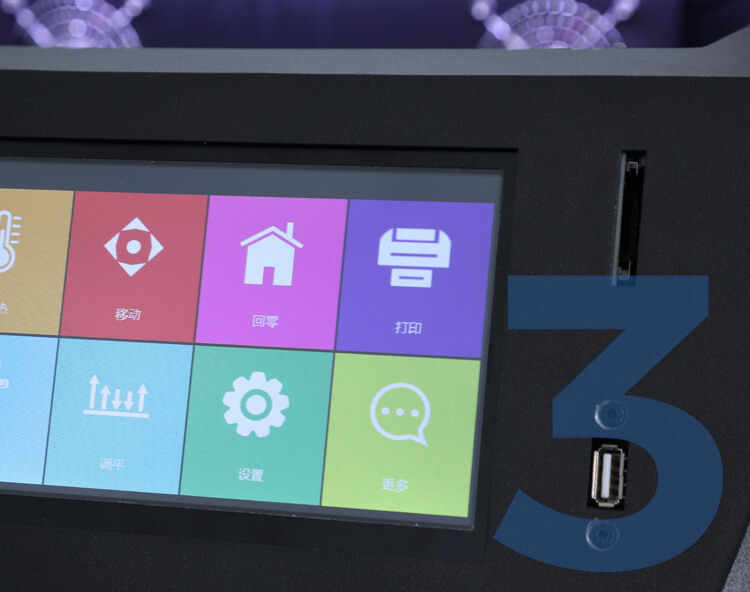

Allow offline printing
Use U disk or SD card to print without connecting to a computer to print. After starting to print, the data is automatically saved and the U disk or SD card can be removed.
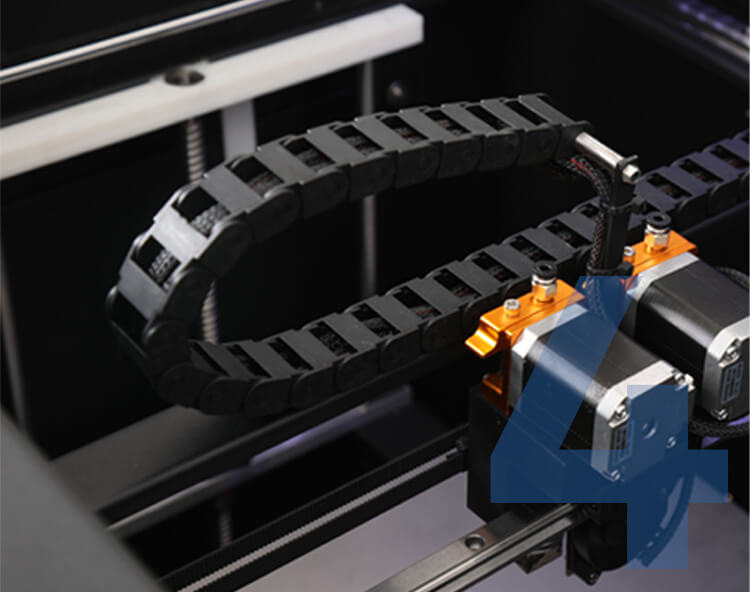

Drag chain wiring design
The wire is installed in the inner casing of the drag chain to effectively ensure that the wire will not be damaged for a long time when the printer moves at high speed.
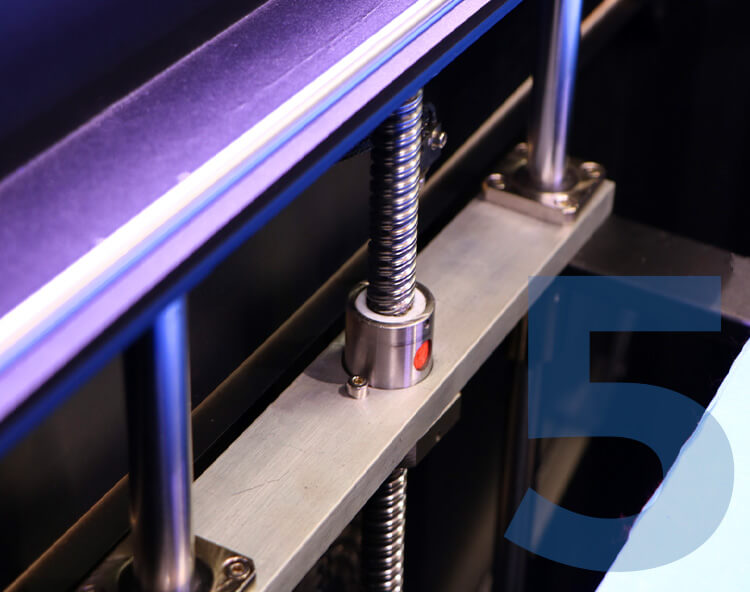

Precision ball screw
Using the latest Taiwan ball screw, it has higher straightness, lower friction coefficient, better smoothness, higher positioning accuracy and more stability during printing.
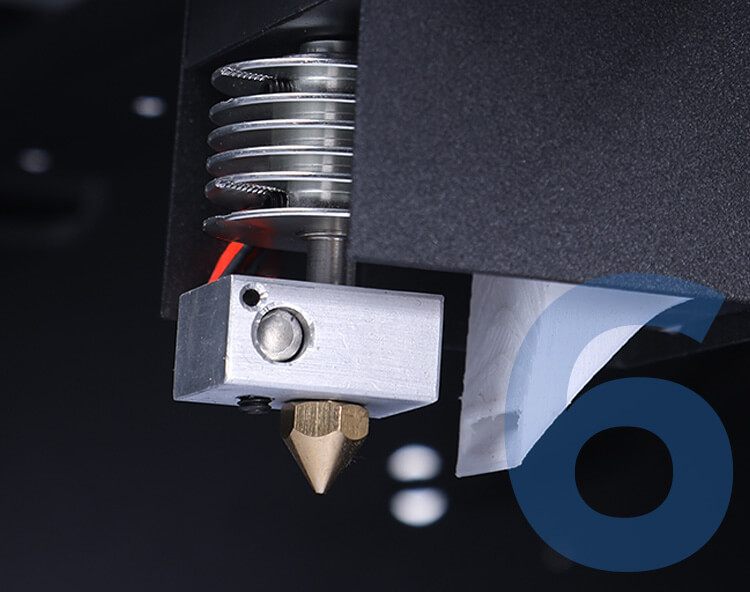

Alloy nozzle
Independently developed a unique bullet nozzle with uniform heating and a patented head assembly, so that it can work smoothly without interruption.
What Our Customers Say
Industrial 3D Printing Machine buying guide
Introduction of 3D Printers on the Market
Buying a 3D printer isn’t as complex as starting or running a business. It’s a straightforward deal, you pay, and the printer of choice is taken to your doorstep. There are different types of industrial 3D printers available in the global market with numerous manufacturers catering to the design and creation. The efficiency of every industrial 3D printer is dependent on its working principle.
To help better understand what it takes to buy a 3D printer, the types available, the modelling processes and the questions you need ask an industrial 3D printer manufacturer before finalizing your purchase, we detailed out this buying guide. All we ask is that, whether you are looking for a low-cost 3D printer or commercial 3D printer for sale, take out time to consider all the factors we detailed out.
1.1, What are the 3D printers with different principles?
Obtaining the best user experience from a 3D printer requires a basic understanding of the underlying principle behind the different variants and designs available. The four dominant industrial 3D printers dictating trends in the printing industry are FDM {Fused deposition modelling}, LCD {Liquid crystal display}, DLP {Digital light processing} and SLA {Stereolithography}.

Fused Deposition Modelling {FDM}: FDM industrial 3D printer is currently the most popular 3D printing technology. It is used in both affordable 3D printers and even 3D pens. FDM printing was originally developed and implemented by Scott Crump from Stratasys, founded, in the 1980s. Other 3D printing companies have embraced similar technology but under different names. A well-known manufacturer MakerBot coined a virtually identical technology, calling it Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF).
Industrial 3D printers which use FDM Technology construct objects layer by layer from the very bottom up by heating and extruding thermoplastic filament. The whole process is somewhat similar to stereolithography. Specialized programs or Slicers “cut” CAD models into layers and computes the manner printer’s extruder would assemble each layer.
In addition to thermoplastic, a printer may extrude support materials too. Then the printer heats thermoplastic until its melting point and extrudes it throughout nozzle on a printing bed, which you may know as a build platform or a desk, on a predetermined pattern determined by the 3D model and Slicer software.
The Slicer software running on the computer connected to the industrial 3D printer translates the measurements of an object into X, Y, and Z coordinates and controls the nozzle and the foundation to follow calculated route during printing.
When the thin layer of plastic binds to the layer beneath it, it melts and hardens. When the layer is completed, the base is lowered to accommodate the printing of the next layer.
Liquid Crystal Display {LCD}: Liquid crystal display printers or LCD printers as they are popularly known are industrial 3D printers use to create 3D models or designs of numerous objects in education, automotive, aerospace, medicine, dentistry etc. LCD printers generate their light source through an array of UV LCDs. These printers are used to create 3D patterns or images of CAD models using materials such as resin, wax or metals. The images or 3D models obtained using LCD 3D printers are composed of dots.
LCD industrial 3D printers display image by sending light from a metal-halide lamp through a prism or series of dichroic filters. This dichroic filter separates light into three polysilicon panels. In simple terms, a liquid 3D printer uses an array of UV LCD as its light source. The printer shines light directly from the flat LCD panel in a parallel fashion onto the build area.
As the light travels through the light source, the individual pixels open up to allow light to pass or close to block the light. This combination of open and closed pixels creates room for the liquid polymer 3D printer to produce multiple colours and shades on the projected image.
The light emitted from an LCD 3D printer isn’t expanded—that’s, it doesn’t spread beyond its projected frame. When using these 3D printers, you can design patterns and images of multiple variations; rest assured you wouldn’t experience pixel distortion halfway. Note that unlike most other resin printers, the LCD industrial 3D printers print quality depends on its LCD density.
Digital light processing {DLP}: DLP is another industrial 3D printer quite much like stereolithography. The DLP technology was made in 1987 by Larry Hornbeck of Texas Instruments and became well known for its use in the production of projectors.
It utilizes digital micromirrors laid out on a semiconductor chip. The technology is found in mobile phones, film projectors, and, of course, in 3D printing. For 3D printing, both DLP and SLA functions with photopolymers. However, the difference between SLA and DLP industrial 3D printers is that DLA requires an additional source of lighting.
3D printing amateurs frequently use more traditional sources of lights like arc lamps for DLP printing. The other important piece of the DLP puzzle is an LCD (liquid crystal display) panel, which gets applied to the entire surface of the 3D printed layer during a single run of the DLP procedure. The substance used for printing is a liquid plastic resin that’s set in a transparent resin container. The resin hardens quickly when exposed to a lot of photons, or more simply put, bright light.

The printing speed for DLP industrial 3D printer is the kicker. A layer of hardened material can be produced with this kind of printer in a few seconds. After the layer is completed, it is transferred, and printing of the next layer is started.
Stereolithography SLA: SLA is an industrial 3D printer which could be used to execute your projects that involve the 3D printing of items. Although this process is the earliest one in the history of 3D printing, it is still in use today.
The idea and application of this method are amazing. Whether you’re a mechanical engineer, who wants to confirm whether the part can fit your design or creative individual who wishes to print a plastic prototype for a fresh upcoming project, Stereolithography 3D printing systems can truly bring your 3D models to life.
SLA industrial 3D printers do not function like normal desktop printers that extrude some quantity of ink to the surface. SLA 3D printers operate with an excess of liquid plastic that after a while hardens and forms to a solid object. Note that parts printed by stereolithography 3D printers usually have smooth surfaces, but its quality depends on the quality of SLA printer used.
After the plastic hardens a stage of the printer drops down in the tank, a fraction of a millimetre and laser forms another layer until printing is finished. After all, layers are printed, the item has to be rinsed using a solvent and then put in an ultraviolet oven to complete processing.
The time required to print an object depends upon the size of the SLA 3d printing system utilized. Small items can be printed within 6-8 hours using a basic kid’s 3D printer, while large 3d prints can be several meters in 3 dimensions and printing time could be up to several days long.
1.2, Why FDM and LCD are the Main Productivity Tools in the Current 3D Market
Industrial 3D printers have gained widespread usage across multiple industries. From jewelry making to research and development in the automotive and aerospace industry, these printers are making wave. However, amongst the four industrial 3D printers we listed out, only FDM and LCD 3D printers are enjoying global prominence. That’s most professionals, and hobbyist in different industries value the three-dimensional glory FDM and LCD printers offer to most other variants available.
Material Difference Between LCD and FDM printers.
LCD 3D printers are industrial resin 3D printers that use plastic resin as the raw material, in contrast to the filament used in FDM technology. The liquid resin used in LCD 3D printing is typically composed of either epoxy or a combination of acrylic and methacrylic monomers. When exposed to UV radiation, these monomers quickly form molecular bonds with each other and turn into a solid polymer.
Thermoplastic materials stand as the most viable printing material for industrial FMD 3D printers. Thermoplastic materials are preferred because of the malleable nature they possess when heated. This remarkable feature gives room for each layer to stick together during the creation process.
The Principle Difference Between FDM and LCD
LCD industrial 3D printers typically display images by sending light from a metal-halide lamp through a prism or series of dichroic filters that separates light into three polysilicon panels. In simple terms, a liquid 3D printer uses an array of UV LCD as its light source. The 3D printing system shines light directly from the flat LCD panel in a parallel fashion onto the build area.
As the light travels through the light source, the individual pixels open up to allow light to pass or close to block the light. This combination of open and closed pixels creates room for the liquid polymer 3D printer to produce multiple colours and shades on the projected image.
The light emitted from an LCD 3D printer isn’t expanded—that’s, it doesn’t spread beyond its projected frame. When using these 3D printers, you can design patterns and images of multiple variations; rest assured you wouldn’t experience pixel distortion halfway.
On the other hand,
For an industrial FDM 3D printer to function properly, it requires a heated nozzle, a build platform, and raw material to build upon. The printing process begins after the modelling software slices the 3D CAD file creating an extrusion path for the nozzle to follow. All necessary support needed by the object is factored into the extrusion path, and the nozzle movement is controlled via the interactive interface found on the machine.

When the software successfully determines a suitable path for the nozzle, the filament is let loosed and fed through the heated nozzle. As soon as the raw material gets to the nozzle, it dissolves to a semi-liquid state and is forced out of the nozzle in the form of super fine beads. Immediately after the material leaves the nozzle, it hardens and bonds to the layer under it.
Using the FMD machine’s mechanical interface, you can lower the platform holding the material to about one-sixteenth of an inch, giving room for the nozzle to start working on the next layer.
The Difference Between FDM and LCD in the Application Area
If you are wondering if FDM and LCD industrial 3D printers can be used simultaneously in a production line; YES, they can. Their durability span across numerous industries and can serve as the perfect modelling machines for every production line.
However, it’s important to keep in mind that these industrial 3D printers serve experts, hobbyist and professionals in different industries. To help you better understand if having an industrial FDM 3D printer and an LCD 3D printer in your production line would heighten productivity, lets list put some of the industries these printers are equipped to serve; if you cater to the needs of clients in the industries listed out for FDM and LCD 3D printers, then you definitely need to have both in your production line.
Application Field for LCD 3D Printers
Jewelry: industrial LCD 3D resin printers also allow multiple designs to be produced in a single print. This means it is very cost-competitive for low production volumes. LCD 3D printers are not restricted by the limitations of CNC machining and can produce parts that were impossible to make in the past. Using a commercial LCD 3D printer, designs can also easily be customized, and a printing experience backed by upgrades that ensure printing comes out perfectly can be easily attained.
Medicine: Medicine, as we know it now, has evolved from a series of discoveries and inventions. New advancements have enabled newer and more sophisticated techniques in medicine, surgery, and healthcare, in general. Wondering how LCD industrial 3D printer manufacturers have helped make this possible? Well, LCD 3D resin printing in medicine has already caused quite the revolution by aiding 3D printing of implants and helping the surgeons with detailed mock surgeries.
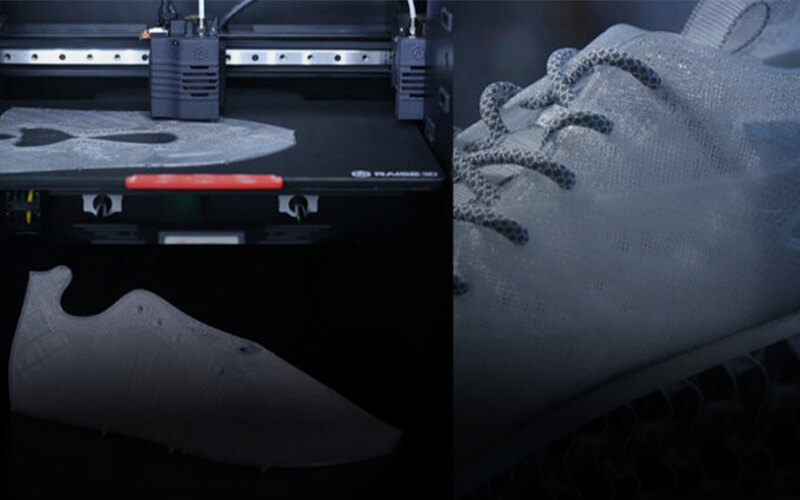
Production and R&D: Ranging from shoe models, electrical parts to finished musical instruments, industrial LCD 3D printers’ have influenced the production cycle. Using an LCD resin 3D printer, hobbyists and professionals in the R&D get to enjoy a 360-degree prototyping process, shorter labour time, accurate finish to complex shoe patterns, and higher efficiency when printing multiple models of different specifications at a time.
Education: Pupils learn best through interaction and application. By doing rather than by reading a book or listening to a lecture. As such, LCD 3D printers serves as an excellent machine to deploy experiential learning and give pupils more hands-on experiences. With an industrial LCD 3D printer, teachers can create activities that take academic concepts from the theoretical to the practical. For example, in biology lessons, students could create an anatomical heart. Such active learning also ensures that pupils retain information with greater ease.
Model Making: with a 3D resin model directing the flow of affairs in a production line, the mode of operation and workflow becomes easy, and durability of the end product is guaranteed. The use of LCD resin 3D printers in the model making creates room for a flawless production line and helps keep R&D experts operating.
Application Field for FDM 3D Printers
Industrial Research and Development: Having an industrial FDM 3D printer when carrying out a research and development task can help you highlight potential risk areas early on. FDM machines allow you to prototype and test small components within a limited time. The machine helps designers access design frameworks and operation sequence conventional R&D processes doesn’t leave much room for.
Production of Animation Figures: FMD industrial 3D printers are regarded as a durable option for creating animations because it grants designers the opportunity to pay meticulous attention to detail while leaving room for even the most minor editing to be carried out. With the best industrial FDM 3D printer at your disposal, you can streamline an animation creation process; rest assured, accuracy is guaranteed.
Model Making: Just like LCD 3D printers, industrial FDM machines are also suitable for creating exceptional models. FDM 3D printer is amongst the few built to sustainably cater to all your printing needs at a low cost. The printing machine is simple to use and easy to set up. Purchasing an FDM machine from our catalog would enable you to enjoy a smooth and efficient 3D printing process right out of the box.
Aerospace and Automotive: industrial FDM 3D printers brought about massive improvements in design, validation, production, and customization. Industrial 3D printer companies impact in the aerospace and automotive industry doesn’t just revolve around the research and development phase—designs and patterns created using FDM 3D printers stand as the bedrock powering the day to day innovations of the aerospace and automotive industry.
1.3, Why we Focus on the R&D of FDM and LCD 3D printers
By now, we believe you are familiar with all the ins and outs of LCD and FDM industrial 3D printers. Since these printers are quite different and serve individuals in diverse industries, you might be wondering why our R&D team is focused on creating formidable LCD and FDM industrial printers; why not focus on one and why do we believe having both in your production line would help heighten efficiency.

First things first, FDM and LCD 3D printers are powering the production line of companies in different industries. And serving those experts and hobbyist better is our primary goal. Our R&D team focus on the design and creation of formidable FDM and LCD industrial 3D printers to help authenticate the viability of the 3D printers in numerous industries.
Also, we know that hobbyist and professionals value getting the best return for their money. With FDM printers being the mainstream industrial 3D printers across multiple sectors and LCD 3D printers standing as the most cost-effective, all the commercial-grade 3D printers available in our store are optimized to provide a high-quality printing experience that allows you enjoy convenient operations without barriers.
Dreambot3D is the 3D printer manufacturer you go to when you require a low-cost 3D printer that is simple to set up, with no goofy plate levelling, no adjustment and no frustration.
How to Choose the Right 3D Printer
We dedicated the whole of chapter one to help you understand the different types of industrial 3D printers available in the global market, the most viable options and why our research and development team have a soft spot for LCD and FDM industrial 3D printers.
Now to the big question, how can I make the right buying decision? Like w stated earlier, buying an industrial 3D printer is not as complex as starting or running a business, but without prior information on all the steps and processes involved, fixing clogged nozzle and bad extrusion can become a part of your day to routine.
In this section, our focus is on the basic factors you need to look out for when choosing a 3D printer. While there are a lot of factors to consider, we have helped you skimp through the noise by shortlisting the three most important factors that determine the type of end-user experience you get to enjoy from your industrial 3D printer.

2.1, Choose 3D printer by Material
The material you want to print on determines the type of 3D printer you should prioritize. As you already know, FMD and LCD industrial 3D printers are not suitable for printing the same type of materials. LCD 3D printers are suitable for printing resins while industrial FDM 3D printers are suitable for printing filaments.
A typical 3D printing process might sometimes require the user to switch materials during design. This might not be termed the day to day experience of a hobbyist or even a professional in the industry, but in as far as you intend to build a career in the printing industry, it’s an experience you are going to someday have to contend with; why not prepare yourself beforehand? There are multiple FDM and LCD 3D printers available, but only a few allow its user to switch back and forth between models and materials.
Tensile strength also plays a vital role in the printing process. Tensile strength, which is regarded as how much pressure a material can withstand before tearing apart, is also a factor to consider when looking for the best FDM or LCD machine for your printing needs.
Most filaments and resins have unique tensile strength, but when the focus is placed on the overall picture, they are not durable enough to withstand the toughness of most of the FDM and LCD 3D printers available.
While there are still factors such as the melting temperature and the material’s durability to consider, their influence on the type of FDM or LCD 3D printer to choose is not as consequential as the above listed.
It’s practically impossible to consider all the material you might ever have to print on using the FDM or LCD 3D printer you are about to purchase, but that does not in any way means neglecting the influence of your printing material on your buying decision is probable.
3D printing can be fun and exciting and at the same time daunting and tiring; it all depends on how much time you invest in making the right buying decision. FDM and LCD 3D printers are durable modelling machines, but if due precaution is not taken during purchase, you might end up with a printer that keeps your print failing for one reason or another.
If you are looking to avoid the frustration and repetitive sequence that comes with using the wrong FDM or LCD industrial 3D printer, we recommend you contact our support team; whether you need a low-cost 3D printer, industrial resin 3D printer, commercial 3D printer for sale, or an industrial FDM printer, Dreambot3D got you covered.

2.2, Select 3D Printer Through Application
With industrial 3D printers rapidly taking over the design and creation process in multiple sectors, it’s impossible to choose the right printer without first analyzing the impact and variability in the field or sector you are operating in.
In recent years, 3D printing has developed significantly and can now perform crucial roles in many applications, with the most important being manufacturing, medicine, architecture, custom art and design.
Industrial 3D printing processes are finally catching up to their full potential and are currently being used in manufacturing and medical industries, as well as by sociocultural sectors which facilitate 3D printing for commercial purposes. There has been a lot of hype in the last decade when referring to the possibilities we can achieve by adopting 3D printing as one of the main manufacturing technologies.
For a long time, the issue with industrial 3D printers was that it had demanded very high entry costs, which does not allow a profitable implementation to mass-manufacturers when compared to standard processes. However, recent market trends spotted have found that this is finally changing. As the market for 3D printing has shown some of the quickest growth within the manufacturing industry in recent years
3D printing has entered the world of clothing with fashion designers experimenting with 3D-printed bikinis, shoes, and dresses. LCD 3D printing is used to manufacture moulds for making jewelry, and even the jewelry itself. Industrial FDM printing is becoming popular in the customizable gifts industry, with products such as personalized models of art and doll.
The use of FMD and LCD 3D printers to produce scale models within architecture and construction has steadily increased in popularity as the cost of 3D printers has reduced. This has enabled faster turnaround of such scale models and allowed a steady increase in the speed of production and the complexity of the objects being produced.
Before finalizing your industrial 3D printer buying decision, note the sector you are operating from, the needs of individuals in the industry and the type FDM or LCD machine that would be able to cater to their needs efficiently. Till you have guaranteed credibility of the selected LCD or FDM industrial 3D printer variant from manufacturers and professionals in the industry, avoid finalizing the purchase.
2.3, By Printing Size
You now the material and the application industry; it’s time to consider the print size. LCD and FDM 3D industrial printers come in multiple variants. Some are suitable for large printing tasks, while others possess printing molds that can cater to only small tasks.
How big is your business, and what size of prints do your customers demand from you regularly? At Dreambot3D, we have seen the irregularities and extra expenses that come with purchasing an LCD 3D printer that’s not compatible with the print size.
Over the years we have been in business, we have had the opportunity of interacting with consumers from different countries and region. One of the most highly influential factors most hobbyist or professionals who have walked through our door to purchase an industrial 3D printer ignore is the size of the print.
Yeah, it’s practically impossible to determine the exact size or specification attributed, or that would be required in most of the prints you make—especially if you are a business owner looking to satisfy the needs of clients from different parts of the world—but totally ignoring the print size an industrial 3D printer can create is unacceptable.

LCD and FDM 3D printers garnered renowned usage ahead of SLA and DLP not just because of their printing speed or the remarkable finish product they are capable of providing, but also because of their ability to perfectly create sustainable 3D models on wide materials.
Before buying any LCD or FDM industrial 3D printer, try to know the type of resin or filament it can print on and whether it’s durable enough to print perfect models on wide materials without leaving distorted edges.
As you already know, we exist to serve you better. All the LCD and FDM industrial 3D printers available in our collection can create prints of any size. You can spare yourself countless hours of stress by contacting our support team today—they would have a resin or filament 3D printer with the desired specification ready for you in no time.
How to Combine FDM and LCD to Better Realize the Application of Printer
The hassle to determine the type of industrial 3D printer to settle for can throw you off balance, especially if you are new to the industry. While it’s necessary to note the basic difference between the two and base your decision on the factors we listed out in chapter 2, its important you also keep in mind that you can work with both industrial 3D printers.
Yes, LCD and FMD industrial 3D printers can serve as durable 3D printing systems for industrial and home use. With both industrial 3D printers at your disposal, you get to save tons of resources.
In the coming sections, a detailed overview of the pecks you get to enjoy from having an LCD 3D printer and an industrial FDM 3D printer in your production line.
Note that while having both FDM and LCD printing equipment might printers be termed costly during purchase, the long-term advantages can help you operate at a preferred pace ahead of the competition.
3.1, Why do You Need Both FDM and LCD at the Same Time
We have been talking about how important FDM and LCD industrial 3D printers are to the design and creation of efficient models. It’s obvious that many professionals and experts would be sceptical about investing in LCD and FDM 3D printers at this same.
While these scepticisms can stand true for individuals catering to a specific client base, same can’t be said for production lines trying to keep up with the diverse needs of individuals from different walks of life.

FDM and LCD industrial 3D printers can help heighten efficiency and hasten the creation process in an unimaginable way. Here are some of the benefits of having both industrial 3D printers in your production line.
Dynamic Modelling Sequence: 3D industrial printers which use FDM Technology construct objects layer by layer from the very bottom up by heating and extruding thermoplastic filament. The whole process is somewhat similar to stereolithography. Specialized programs or Slicers “cut” CAD models into layers and computes the manner printer’s extruder would assemble each layer.
While LCD 3D printers display image by sending light from a metal-halide lamp through a prism or series of dichroic filters, this dichroic filter separates light into three polysilicon panels. In simple terms, a liquid 3D printer uses an array of UV LCD as its light source. The printer shines light directly from the flat LCD panel in a parallel fashion onto the build area.
Remarkable Features: With both commercial 3D printers, you get to enjoy a printing process built on flexibility, durability and efficiency. Industrial FDM printers support operational sequences that boost your confidence to try out new models and create fun and useful things all through a custom button that easily loads and unloads filament.
LCD 3D resin printers are semi assembling systems not susceptible to print fails; that’s you can enjoy around the clock printing operation with this industrial FDM printers.
Suitable for Professional, Industrial and Household Setting: while LCD and FDM industrial 3D printers are optimized to cater to the dynamic needs of individuals in different industries, their reliability only goes as far as their 3D printer components can offer.
FDM printers are not reputable enough to provide the smooth finish LCD provides in a commercial setting the same way; LCD printers are not durable enough to serve as in a household setting. Together, FDM and LCD 3D printers can help you enjoyed all-round sustained printing solutions.
3.2, What Resources can Be Saved for You by Combining FDM and LCD
Since you now know why you need FDM and LCD industrial 3D printers, it’s no news that you might be wondering what you would gain from having LCD and FDM industrial printers in your production line; that’s what resources can you save from running a production line where FDM and LCD 3D industrial printers take precedence.
Time: time as you already know is not just money, time is everything. More time means more opportunities, more production, more output, more relevance, simply put, more time begets more room for growth.
Now, in an industry where every professional and hobbyist is looking to put their best foot forward, smart works must be backed by hard work.
With an FDM and LCD industrial 3D printers at your disposal, you get to enjoy a whole new level of productivity. You can take on your daily task rest assured your mode of operation is solidly backed by machines guaranteed to provide the best possible output.
So, whether you a are a hobbyist who fell in love with the simple yet artistic thrill of 3D printing, or you are a professional who wants to heighten his or her daily input to a considerable level, having LCD and FDM printing system at your disposal would go a long way.
Material: the difference in printing material is a common trend in the printing industry. Not all resins can possess the durability needed to print specific household items the same way not all filaments can handle the high temperature needed in printing 3D models in the medical industry.
With FDM and LCD 3D printers at your disposal, you get to print on Standard thermoplastics, such as ABS, PLA, and their various blends and Varieties of resin (thermosetting plastics). Standard, engineering (ABS-like, PP-like, flexible, heat-resistant), castable, dental, and medical (biocompatible).
As a hobbyist or professional in the industry, the only way to obtain the balance needed to provide all-round satisfaction to clients is by operating with machines capable of meeting their dynamic needs on both ends.
With an FDM and LCD industrial 3D printer, this simple yet highly valued goal becomes possible. LCD printers provide the flexibility needed to print resins while FDM is notable for its ability to create remarkable 3D models out of filaments.
Money: it might not always be about profit, but it’s always about the money. Most of your day to day workload is built around satisfying the dynamic needs of your clients so they can pump in funds that keep the production line functional and your family well-fed.

With an FDM or LCD 3D industrial printer, there is no doubt that you would be able to obtain the funds needed to keep your production line functional, but with regards to the inflow and outflow of funds, you will easily come across limiting barriers.
At Dreambot3D, we optimized all our LCD and FDM industrial 3D printers to help our clients keep the production line running all year long. If you have finalized your decision to inculcate LCD and FDM 3D commercial 3D printers into your production line or you prefer specializing in modelling filament over resin or resin over filament, Dreambot3d got you covered; get in touch today and we will have an FDM or LCD 3D printer of choice shipped to your doorstep within 3 to 5 business days.
3.3, Combining FDM and LCD Case Reference
Combining FDM and LCD 3D printer is the fastest way to heighten productivity, print in different orientations and enjoy the excellence tolerance that comes with 3D printing. To further demystify the endless potentials and opportunities having LCD and FDM industrial 3D printers in your production line offers, let’s look at the proficiency you get to enjoy from using LCD and FDM industrial 3D printers.
Work Flow and Ease of Use: The workflow for both FDM and LCD 3D printing system consist of three steps: designing, 3D printing, and post-processing. First, use any CAD software or 3D scan data to design a model, and export it in a 3D printable file format.
Once the 3D printing process begins, most 3D printers can run unattended, even overnight, until the print is complete. Both FDM and LCD industrial 3D printers use support structures to facilitate 3D printing more complex geometries, and their removal represents the last step in post-processing.
Precision and Accuracy: industrial FDM 3D printers form layers by depositing lines of molten material. With this process, the resolution of the part is defined by the size of the extrusion nozzle, and there are voids in between the rounded lines as the nozzle deposits them.
As a result, layers may not fully adhere to one another, layers are generally clearly visible on the surface, and the process lacks the ability to reproduce intricate details that other technologies can offer.
In LCD 3D printing system, liquid resin is cured by a highly-precise laser to form each layer, which can achieve much finer details and is more reliable to repeatedly achieve high-quality results. As a result, SLA 3D printing is known for its fine features, smooth surface finish, ultimate part precision, and accuracy.
How to Buy a Suitable 3D Printer
We have come a long way. From what 3D printers mean, to how they operate, to the process involved in choosing the right industrial 3D printer and the need for LCD 3D printers and industrial FDM 3D printers in your production line, we have covered it all. Now to the main focus of this buying guide, how can you buy a suitable 3D printer?
Since it’s impossible to detail out all the steps processes and procedures involved in a single sentence, we have broken them down into seven distinct factors. Before settling for any industrial 3D printer or contacting any manufacturer to actualize your purchase, we recommend you consider these factors.
4.1 Choose a Reliable Brand
For most professionals in the printing industry, it all comes down to brand. Hundreds of brands have built a formidable reputation for themselves by offering industrial 3D printers with remarkable features. While it’s essential you check out a brand’s track record and reviews from previous customers, it’s also important you don’t base your buying decision entirely on a brand’s name.
There are a lot of industrial 3D printers available world-wide with reputable brand tags but void of the innovative design and features required to keep your printing line functional. Many brands built a good name for themselves in the early 90s but haven’t been able to keep up with the diverse changes needed to excel in the 21st-century market.
Before putting hours of research into exploring a brand’s portfolio or track record in the global market, make sure the 3D printer you want to buy possesses features in line with your needs and has been ascertained satisfactory by other users and experts in your industry.
There are so many 3D printers being developed and released into the market every day. While most of these printers meet the basic requirements and features of SLA, FDM, LCD, SLS, DLP printers, you should not be hasty while sealing the deal yet. Why? You may ask.
3D printers are not cheap machines. You’ll part ways with a considerable amount of your money; therefore, you must ensure that you get value for your money. While your choice should not solely be made on the brands’ name, it is crucial that you do thorough background research on the company’s Google ratings and reviews before making a purchase.
Consider buying your printer from an industrial 3D printer manufacturer that has a good track record, a higher rating on Google, and a genuine customer support system. Such a company will be apt to respond to all your urgent needs, for instance, if your printer breaks or runs out of filaments. The company/brand that you’ll pick for your printer can make or break your printing experience if something goes amiss.
4.2 Safety Configuration of the Machine
You have made up your mind on the LCD 3D printer or industrial FDM 3D printer you want to purchase. You have set your needs and that of your client base ahead of budget, and you are all good to make payment; Wait! one more thing.
What’s the safety configuration of the machine-like? Hope you are not about to purchase a ticking time bomb? Industrial 3D printer’s safety configuration can look complex, especially during rough situations. Explore the dos and don’ts of the machine’s safety configuration, know where and where not to press in case of overheating, and above all, make sure your purchase is backed with an instructional guide.
Most reliable 3D printing equipment manufacturer provides support to enable you to navigate your way around the 3D printing equipment before finalizing your purchase. However, if such services are not provided by your preferred LCD or FDM industrial 3D printer manufacturer, use the instructional manual provided to explore the safety configuration before finalizing your purchase.
If you are of the notion that this process is quite complex and require assistance understanding the intricacies involved, we recommend you visit our industrial 3D printer catalog; our support team would guide you through the buying process.
4.3 Resolution Requirement of the Machine
3D printing resolution is the level of detail quality at which your part is created. Industrial 3D printers extrude plastic through a nozzle to create 3D printed objects. That nozzle pin can be adjusted to different widths to allow for higher or lower resolution printing. It’s necessary that you keenly take into account the resolution of a printing machine before buying one depending on the industry you are operating in.
While the resolution requirement of an industrial 3D printer is regarded as the number one factor to consider when making a 3D printer purchase by experts in numerous industries, this can be referred to as a myth that doesn’t apply to all. The resolution of an FDM or LCD 3D printer determines the clarity and precision that can be enjoyed from a given 3D model and pattern.
However, the resolution of a 3D printing system used in the animation industry doesn’t have to be on the same level as the one used in the jewellery or engineering industry. When looking at the resolution requirement of an industrial FDM 3D printer, it’s important you take into consideration the industry you are operating in. In which industry do you want to use the machine? What sort of models do you want to print? How clear or precise does the model have to be for it to be termed efficient?
Answering the above-listed questions would help you demystify some of the myths attached to buying a 3D printer. Yeah, buying a high-resolution industrial 3D printer should be considered a priority if the funds and budget to finance it is available. But in scenarios where you are on a budget, you can save cost by analyzing the machine usage and model requirement.
Industrial 3D printers come in different variants, shapes, and sizes, optimized with a fitting design and resolution. At Dreambot3D, our daily task revolves around catering to individuals’ dynamic needs and desires from numerous parts of the globe. We know how daunting navigating a machine with a proper resolution can be.
Dreambot3D core value is to provide satisfactory all-round services. To keep up with this mission, we offer a support team that can help you understand the resolution requirements of multiple machines, the industries they are optimized to serve, and direct you towards multiple variants that would serve you better.
Note that while the quality of print detail is more paramount in some industries than it is in others, the resolution of a machine decides how fine the details of your part will be. A lower resolution less quality and low details on the print object. The objects will have smooth surfaces at the expense of extra filament usage and time consumption. A high resolution, conversely, gives fine quality and better details on print objects.
4.4 Consider Whether the Price of the Machine is Acceptable
LCD and FDM industrial 3D printers are quite expensive. A good industrial 3D printer requires an investment well above a thousand dollar. Budget and pricing is a basic factor that must be considered before you kickstart the buying process.
While most of the renowned printing systems available are quite expensive, don’t make the mistake of basing the efficiency or durability of a commercial-grade 3D printer on the price tags attached. There are lots of LCD and FDM 3D printers offering high-quality printing services at cost-efficient rates.
If you run a big production line or you are a hobbyist looking to purchase a remarkable 3D industrial 3D printer, and you firmly stand by the belief that your budget is sizable enough to purchase any printing machine of choice—we recommend you explore our catalogue armed with the basic features and specification you require from a preferred FDM or LCD 3D printer.
On the other end, if you are on a low budget and require something substantial to cater to your day to day printing needs, please put a call through today—our support representative will guide you through the buying process.
Sometimes people tend to purchase 3D printers based on the price only. The price of a 3D machine plays a big role in decision making. But with so many industrial and commercial 3D printers available for sale at the consumer level today, you must keep a keen eye on the machine’s brand, resolution, and safety configuration.
4.5 Consider the Suppliers After-sales Service Capability
Many folks place all their focus on the remarkable features a machine offers and forget to obtain detailed info on what their suppliers after service capability is like. From experience, we can boldly tell you that a remarkable LCD resin 3D printer or an industrial FDM 3D printer with no warranty policy guiding its purchase would do you more harm than good.
Every reliable industrial 3D printer manufacturer attributes a warranty policy of not less than one year to each product available in its collection. If you are about to purchase a 3D printer and a warranty policy of less than one year is thrown your way, abort purchase.
Also, take note of technical support. 24 hours support service is ideal. However, there are a lot of formidable industrial 3D printer manufacturers not offering round the clock support. Before finalizing your purchase, try to ensure that the brand you are banking with possesses technical support with a viable track record.
4.6 Consider the Service Life of the Machine
The service life for most industrial 3D printers is about 5 to 10 years. While the warranty policy on most 3D printers doesn’t grant you access to refunds or after-sales privileges 1 or 2 years after purchase, purchasing an industrial 3D printer from a reliable manufacturer comes with the guarantee that your machine will be in shape and keep your production line running for at least five years.
With that being said, it’s important to note that the estimated service life of the machine can change at any time based on external factors. How you use your machine determines how long it would last. If you leave you industrial FDM 3D printer or LCD resin 3D printer packed dirty on a regular, you shouldn’t expect the ten years life expectancy to hold any ground.
If you went gone through the hassle of finding the right industrial 3D printer manufacturer, inspecting all the necessary features and finalizing the purchase, you wouldn’t want the whole effort you put in to go down the drain based on negligence from your part. If you try as much as possible to keep your industrial 3D printer clean and in good shape, service life expectancy wouldn’t be an issue.
4.7 Consider the Maintenance Cost of the Machine
Still, on the time topic, we need to touch onto maintenance. 3D Printers require constant maintenance. The print bed must be cleaned between prints or failures are more likely. The moving parts need to be oiled/greased once in a while. Nozzles have to be replaced. LCD screens will need to be replaced. This maintenance applies to ALL printers, whether they are out of the box ready or not.
This is where buying a kit printer is helpful. By building the kit, you learn the ins and outs of how to maintain your printer. Buying an out of the box ready printer simply means you can get a few prints done before you have to learn the same lessons.
Maintaining an FDM or LCD 3D printer takes less effort. Only the Z-axis moves. Everything else would either be a wear and tear item (i.e. just replace the item when it finally fails), or a routine task that has to be done for every print anyway. FDM/FFF printers have those routine tasks too — such as levelling the print bed. However, there are more moving parts which mean more possible points of failure/maintenance.
3D Printing is not as fast as the Star Trek Replicator devices. It takes time to build a 3D object. Smaller objects can be created in 15 minutes or so, but larger objects can take many hours or even days to print. Some printers are faster than others. That speed though is a result of the individual 3D Printer design and how the printer is tuned. Tuning a printer is part of the maintenance time.
Dreambot3D is an industrial 3D printer manufacturer offering highly efficient 3D printing machines with minimal requirement for maintenance. With just regular cleaning, your Dreambot3D industrial 3D printer can stay functional for 5+ years.
FAQ Guide
What companies make 3D printers?
3D printers are products of the research and development industry. Companies involved in the manufacturing of industrial grade production line equipment’s are known as major pioneers of the 3D printing system. If you are looking to buy a 3D printer, there are lots of manufacturers with different variants of 3D printers available. It’s advisable you check the track record of the manufacturer you want to buy from before finalizing your purchase.
Will 3D printers replace manufacturing?
The manufacturing industry and 3D printing are a dream team. Manufacturing is an ever-growing industry, and 3D printing is now at the lead of many advancements and innovative techniques. Potentially, many, many years from now 3D printing will expand to replace traditional manufacturing as we know it today. However, this is not likely something we will see in our lifetimes. In the near future, 3D printing could potentially significantly modify some processes within the industry. Rather than seeing 3D printing as a potential ender of manufacturing as we know it, we see 3D printing as a way to expand the field of manufacturing beyond what we can currently even imagine.
Is there a demand for 3D printing?
The market for 3D printing materials is growing rapidly. Demand is increasing, with more companies buying additive manufacturing (AM) hardware and scaling their AM usage. In 2019, the AM materials market is valued at $1.5 billion. In the next five years, it’s expected to grow into a whopping $4.5 billion opportunity. With such an opportunity at hand, material suppliers, particularly giant chemical companies and metal producers, are becoming increasingly involved in the industry. Alongside developing new materials, they are contributing heavily to the industrialisation of AM.
Is 3D printing the Future?
The advancements in the hardware, software, materials and applications suggest that 3D printing will eventually become yet another manufacturing technology. Naturally, the adoption rate of 3D printing will increase over time, with some segments like dental almost entirely switching to 3D printing. The growing awareness of 3D printing and its benefits will facilitate this growth. In the meantime, the competitive 3D printing landscape will require companies to differentiate themselves from competitors by leveraging their unique expertise and developing a clear value proposition.
What 3D Printer should I buy in 2021?
Is it worth getting a 3D printer?
You Don’t Need a 3D Printer! If you’ve never had the urge to 3D print something before, a 3D printer may not be for you. If you’re interested in 3D printing, you can look at models, modify them, or design your own and have them printed on someone else’s 3D printer. If you love the experience, you may want to consider getting your own 3D printer. If it seems like a hassle or you’re not sure what’s practical or useful to make, you saved a lot of money you might have otherwise spent on a 3D printer! Note that if you just want to 3D print an occasional object, this is probably more cost effective and easier than buying your own 3D printer. You can dabble with 3D printing without owning your own.
How much does it cost to get 3D printed parts?
The cost of a 3D printer 3D printers are based on very different types of technologies. From simple $200 FDM machines to the most sophisticated ones, the cost of a 3D printer can vary by tens of thousands of dollars. If you are thinking of buying your own, you need to figure out which technology will match your needs
Is 3D printing Cheaper than injection molding?
3D Printing is often considered to be more expensive than injection molding when used as production manufacturing process at higher volumes. But that is simply not the case any more. In many situations, 3D printing is more affordable due to the implementation of large scale 3D printing farms, such as Slant 3D, which utilize hundreds of printers operating 24/7. In this case it is estimated that a mold would immediately cost the client $5000 to have manufactured. Now molding costs do vary depending on the size and shape of the part and where it is made. But, on the whole, when you consider design time, iterations, and the spectrum of mold sizes, $50 However, the 3D printing cost per part is only $0.70 per part, and there is no initial investment to get set-up.00 is a very good average. After the mold is made the price per part is $0.20.
How strong are 3D printed parts?
3D printed parts are strong enough to be used to make common plastic items that can withstand great amounts of impact and even heat. For the most part, ABS tend to be much more durable, though it does have a much lower tensile strength than PLA.
How hard is it to learn 3D printing?
It’s not difficult to learn, just an overwhelming number of things that you’d need to learn. But if you’re good at math then it’s not that difficult. Or if you’re good at sculpting or carpentry and stuff. If you can build Ikea furniture without a manual and within an hour then you should be able to understand the concept of 3D… Still, the whole 3D printing world is a simplified version of Computer-aided design/Computer-aided manufacturing where the CAD is you modelling a model in 3D with software and the CAM is sending the model to the 3D printer for the final result. Both techniques are decades old already but are now brought to the masses through 3D printing. The CAM part of 3D printing is hardware dependent. You generally need a 3D printer that uses one of the many techniques to make a 3D model from filament, resin or other materials. But you can also use a CNC machine where the machine basically cuts away parts that are not part of the model.
What software do I need for 3D printing?
TinkerCAD is a browser-based 3D modelling program ideal for beginners. You can save your designs online or share them with others. Export *. stl files to print with your own 3D printer or send your designs to one of popular 3D printing services.
What can you make with a 3D printer?
Among the items made with 3D printers are shoe designs, furniture, wax castings for making jewelry, tools, tripods, gift and novelty items, and toys. The automotive and aviation industries use 3D printers to make parts. Artists can create sculptures, and architects can fabricate models of their projects. Archaeologists are using 3D printers to reconstruct models of fragile artefacts, including some of the antiquities that in recent years have been destroyed by ISIS. Likewise, paleontologists and their students can duplicate dinosaur skeletons and other fossils. Check out our gallery of simple and practical 3D printer objects.
Is 3D printing cheaper than manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing allows production costs to stay the same rather there are one or a thousand units. This has several implications: it makes production available to small businesses that don’t have access to expansive funding and don’t know in advance whether they’ll have many buyers; it reduces the time between conception and sale; it allows each piece to be customized and unique; it allows greater risk-taking by reducing the cost of failure. Second, additive manufacturing reduces lead time for short production runs and permits the creation of very complex shapes without added costs. However, additive manufacturing is still less competitive than traditional manufacturing when it comes to mass production, perfectly smooth finish, production of very large objects and the use of certain materials.
Will 3D printing replace injection molding?
No, 3D Printing Won’t Replace Injection Molding 3D printing offers several advantages over injection molding, but that doesn’t mean it will replace it — at least not anytime soon. Injection molding requires the use of a specialized machine. Injection molding machines can typically create objects faster, more efficiently, and in many cases, with better dimensional accuracy than 3D printers. However, bear in mind 3D printing processes are constantly evolving. Researchers and manufacturers are refining their 3D printing processes to improve the performance of this manufacturing process—there is no saying what will happen in the future.
What is the best industrial printer?
There are hundreds of industrial printers available with new manufacturers venturing into the industry every year. Pinpointing the best industrial printer depends on your printing needs and the type of material you want to print on. However, it’s essential you settle for either LCD od FDM 3D printing systems—they provide renowned printing solutions you wouldn’t find elsewhere.
How much are commercial 3D printers?
DLP/SLA on the market is expensive to reach 10,000-100,000 US dollars, but our LCD only costs 500-3500 US dollars, even our largest industrial LCD is only 10,000-15,000 US dollars.
Can 3D printers be used for mass production?
Yes, 3D printers can be used for mass production. However, Mass production with 3D printing doesn’t always mean directly printing end-use parts, but creating cheap, custom tooling. An example is custom 3D printed molds for injection molding. For low-volume production (approximately 10-100 parts), 3D-printed molds save time and money. They also enable a more agile manufacturing approach, allowing engineers and designers to easily modify molds and continue to iterate on the design of functional end use parts, challenging what it traditionally means to “ship” a product.
How durable are 3D printed items?
It can depend on the type of material you use, but even cheap ABS and PLA is extremely durable. For seriously strong stuff you can use Petg, Polyflex Polymax and flexible materials. But yes – parts are as good as commercially produced parts, in many cases stronger and lighter. To a large extent for FDM machines it depends on the orientation you print them in. So the same part can be printed in different orientations and one will be weak and break easily and the other will be strong, flexible and hard to break. Getting really good 3d printed parts is as much an art as a science.
What is the strongest plastic for 3D printing?
The most popular desktop filament is probably polylactic acid, or PLA. We print PLA with the heated bed at 60 degrees Celsius and a coat of Wofbite Nano. It’s also best to keep the lid off as PLA is sensitive to high temperatures. PLA is an environmentally friendly, compostable filament that prints easily at low temperatures and looks great. It’s also pretty strong. It’s pretty darn impressive that PLA survived up to a 285 lb lift. We probably could have eked a few more pounds out of it, but the hook was already yielding. Truth be told, we were surprised with PLA’s strength. However, with a tensile strength of 7,250 psi, this is a strong material. With that comes a caveat, In this case, a caveat that can swallow the entire utility of PLA. Because PLA is biodegradable, don’t be surprised if it starts breaking down during use. In the sun especially, PLA is unpredictable and can change forms with a few hours. So please don’t print your tow hook out of PLA — it should not be used for anything supporting a load. Stick to what PLA is best for, toys and figurines.
Can a car be 3D printed?
When it comes to the automotive industry, additive manufacturing is a major game-changer. 3D printing technology used to be only a prototyping tool – and obviously, it still is. But now it’s also starting to be used in car manufacturing. You read it right, we can now build cars using 3D printing. This is the result of a global tendency in the world of additive manufacturing: this technology is now recognized as one of the serious manufacturing technologies, and not just as a way to build a good proof of concept or prototype
Is PLA cancerous?
A limited study back in 2013 by researchers from the Illinois Institute of Technology and The University of Texas at Austin suggested that ABS and PLA filaments do release some unhealthy particles into the air during 3D printing, but those same researchers are now back with a more comprehensive study. And the results are not very good – when 3D printing certain filaments in confined spaces, high levels of possibly carcinogenic (cancer-causing) particles can be measured in the air. This has become apparent from a study entitled Emissions of Ultrafine Particles and Volatile Organic Compounds from Commercially Available Desktop Three-Dimensional Printers with Multiple Filaments, which has just appeared in the journal Environmental Science & Technology.
Is PETG stronger than PLA?
PLA (Polylactic Acid) is a polyester plastic and is a consumer favourite for 3d printing, for most first-time printer’s PLA is the go to filament to test and play before venturing on to more difficult materials. PETG stands for “Polyethylene terephthalate glycol-modified” and the normal reputation is that it is as easy to print as PLA but has the physical properties of ABS. Both are user friendly and PLA is slightly easier to 3D Print than PETG. This is due to PLA being more forgiving when it comes to settings. However, PETG is more durable, stronger and is impact resistant.
What happens if you print PLA too hot?
Printing PLA till it becomes extremely hot can cause damage to your model. Its recommended you try as much as possible to regulate the temperature when printing or designing a model using PLA. If your layers aren’t adhering to one another, heating up your hot end can usually fix it. Cooling the hot end, on the other hand, can help with print quality. If the extruder is too hot, the PLA filament can become extra soft and flimsy. This can cause your prints to be messy and droopy.
Will PLA melt in the sun?
PLA would be a non-starter for outdoor use as it’s biodegradable and can breakdown in sunlight. Albeit slowly, but won’t be useful for long term project. ABS would be a good choice for longevity, as it can last in outdoor situations for quite a while. Its glass transition temperature is above 100 degrees Celsius so it’ll last in most climates. As for strength ABS is one of the better choices out there, also it’s slightly softer than PLA meaning it will flex before breaking, PLA is much more likely to shatter. ABS is well known for warping while printing though. Not a huge problem though, if you’re used to printing with it.
How many hours will a 3D printer last?
It’s difficult to give a specific value for lifetime hours for a 3D printer but based on my research from reading user experiences, I’d give a range of 7,500 printing hours to 15,000 printing hours (printing for 4 hours every day for 10 years).
Conclusion
You now know what it entails to purchase an industrial 3D printer. Industrial FDM 3D printers and LCD 3D printers are the most sought out 3D printing equipment globally. While they both operate on different principles, in different industries and with different materials, they are both suitable for use in the same production line.
With numerous industrial 3D printer manufacturers priding themselves with the banner of top-notch highly efficient printers, it’s hard to detect which industrial 3D printer company offer low-cost 3D printers that actually possesses such attribute.
If you are tired of scouring the internet and need an industrial 3D printer manufacturer that provides LCD and FDM 3D printers offering greatly improved detail and precision, not susceptible to print fails, an integrated computer board for printing directly from USB, and a user-friendly system that gives you the confidence to try out new models, get in touch; Dreambot3D got you covered.
Dreambot3D