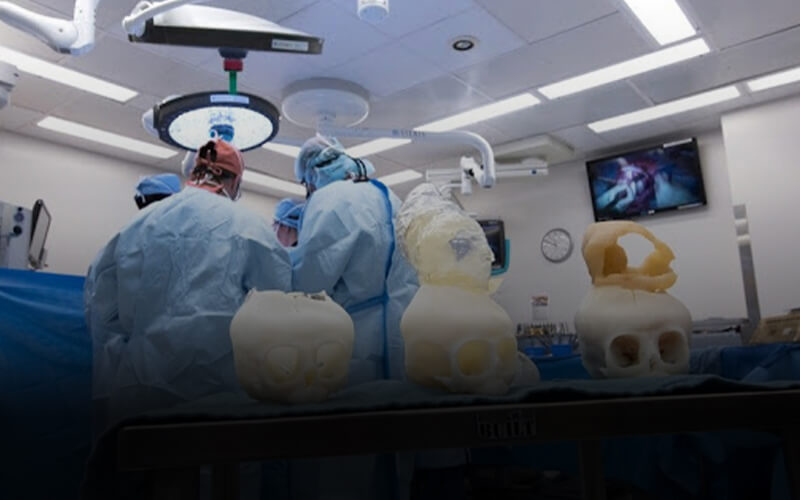
3D Printer Filament Manufacturer
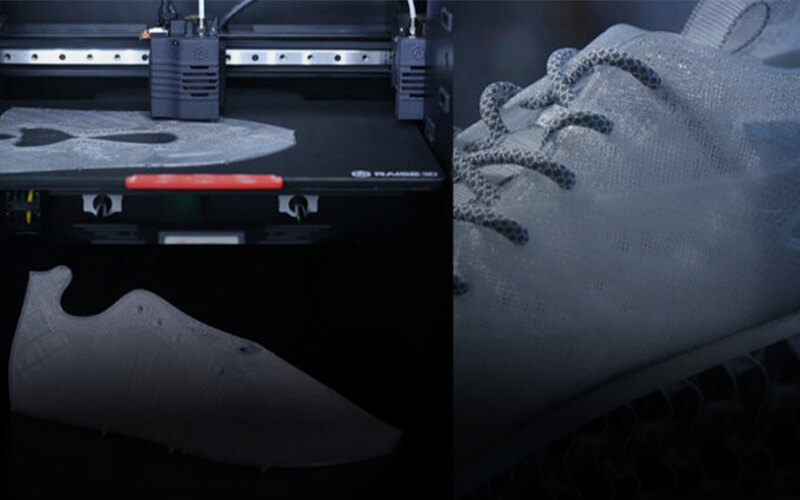
The 3D printer filaments are those materials that are used for 3D printing. These materials include ABS, PLA, PC, Nylon, PVA, PETG, Carbon fiber etc.
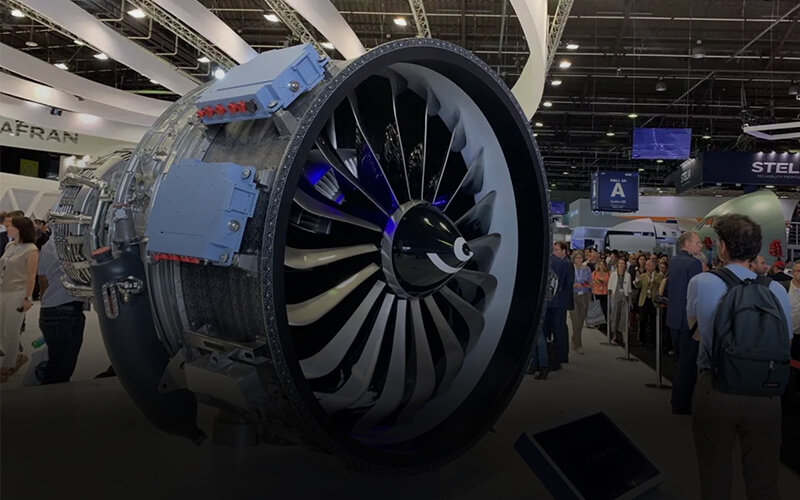
Dreambot3D, as a top 3D printer filament manufacturer, produces filaments with a diameter of 1.75mm and is used in aerospace, automotive, anime, etc.
These 3D printer filaments produce highly detailed finished products with a very smooth forming surface.
3D Printer Filament
The 3D printer filament uses strong materials like ABS, PLA, PC, Nylon, Carbon fiber, etc, for printing 3D prototypes. The 3D printer filaments manufacturer creates filaments with outstanding thermal and chemical resistance.
Each printer filament has a diameter of 1.75mm and a total length of 330m that extrudes layer after layer for an accurate and efficient printing process.
Any of these 3D printer filaments can be used in industries like aerospace, construction, automotive, toy making, etc.
The filaments create high precision printing, edges of printed objects do not wrap, no bubbles when extruded from the nozzle and good liquidity are all benefits of the 3D printer filament.
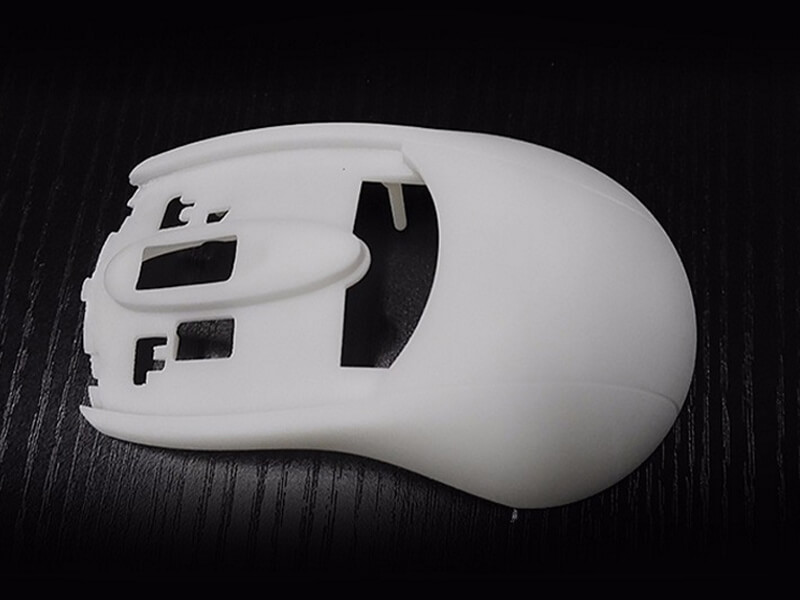
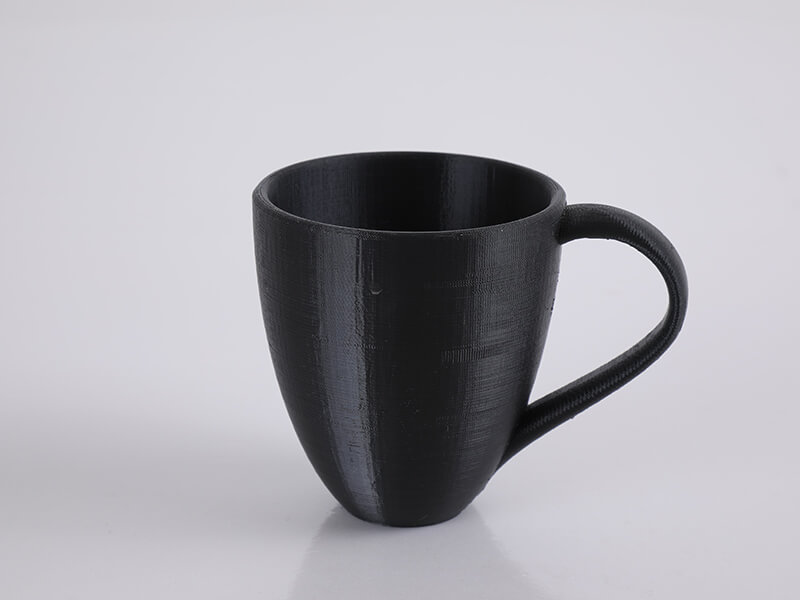
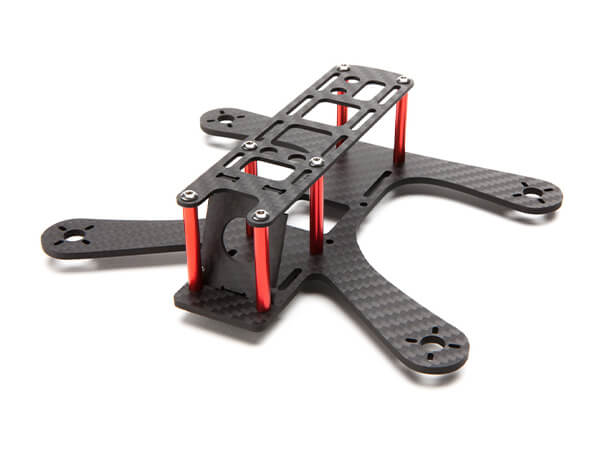
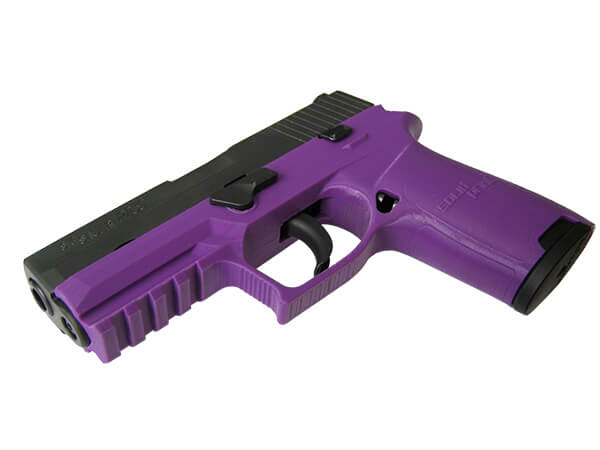







Dreambot3D 3D printer filaments list
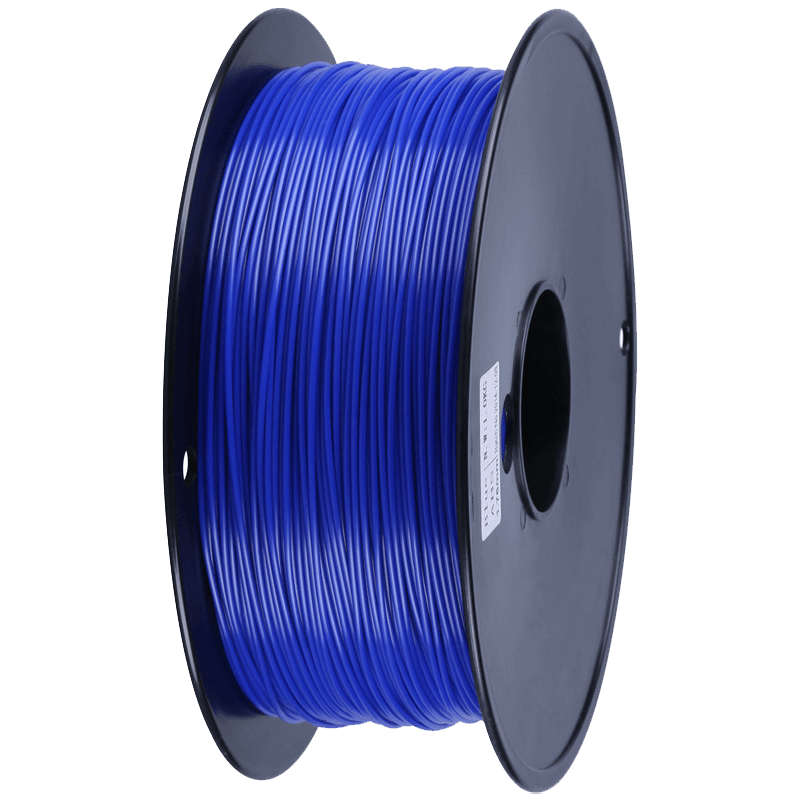

The PLA material is mostly used because of its toughness and removes brittleness. This material is easily degraded and pollution-free.
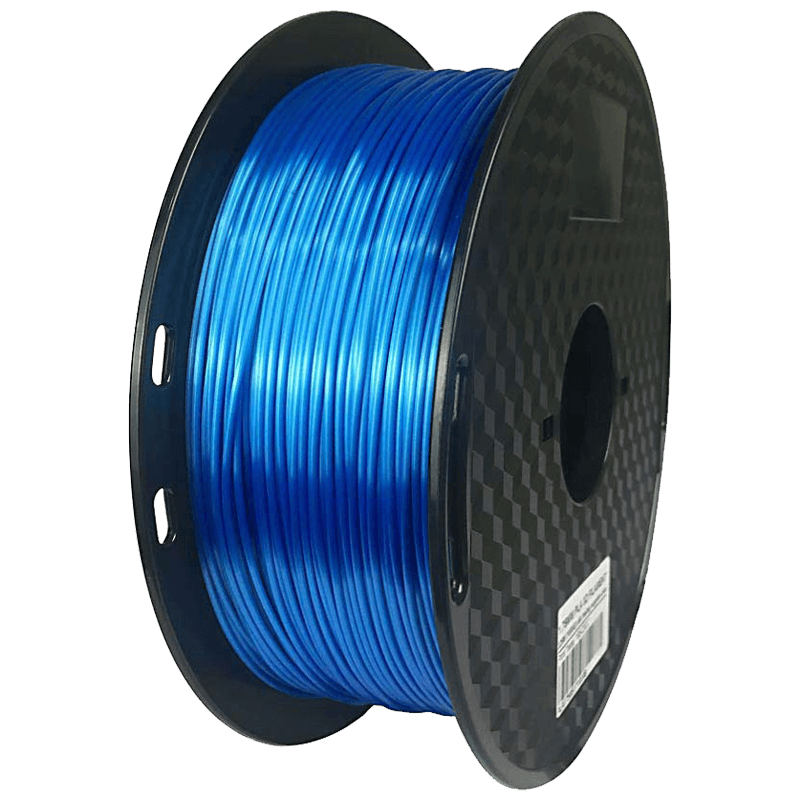

ABS has a good adhesion with other materials. It is easy to print with, coated and plated. This is a non-toxic material.
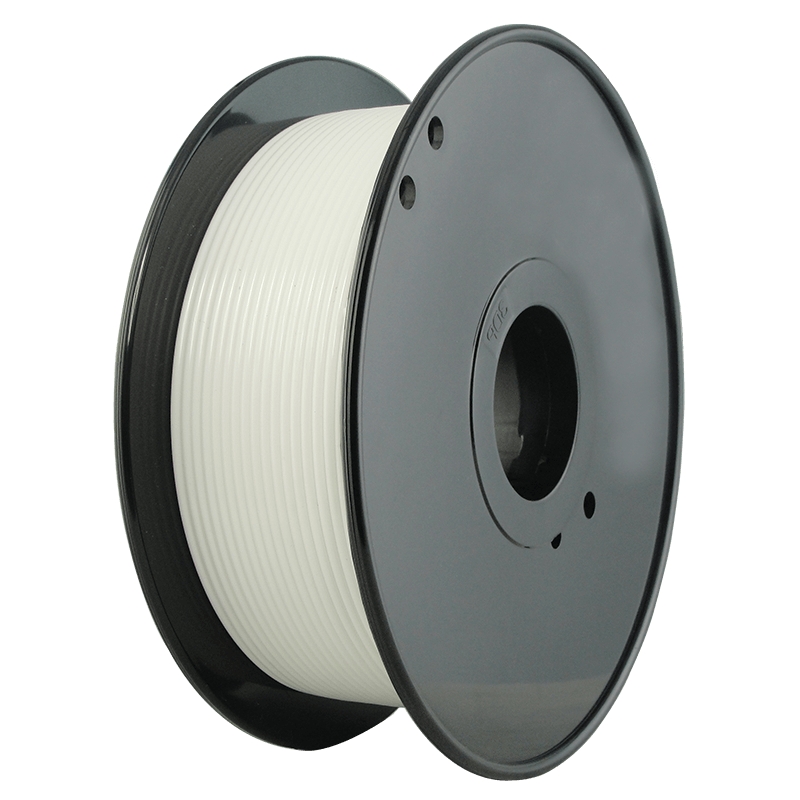

Polycarbonate (PC) is a hard sturdy material that has an outstanding impact resistance and durability. It is able to withstand high temperatures.
TPU is abrasion resistant and it is highly resistant to many temperatures. It is used for printing due to its versatility.
Nylon has a high mechanical strength, a high softening spot, resistant to heat and wear, non-toxic, resistant to harsh weather.
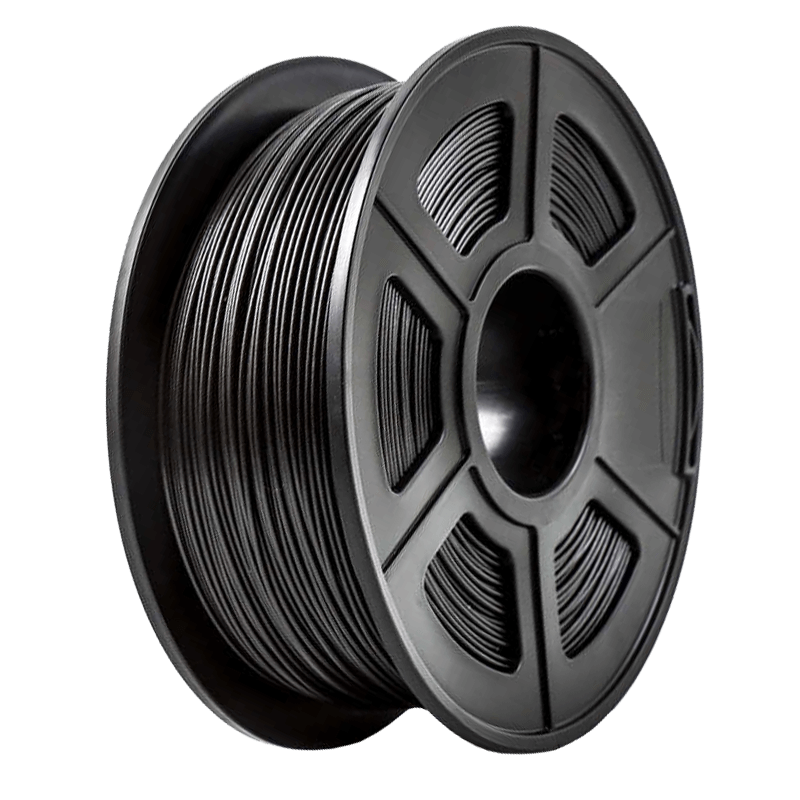

Carbon fiber is a combination of fiber and nylon materials. This makes the material to have a higher modulus and rigidity.

Test your part
We provide sample testing service, allowing you to check the working quality of our 3D printer before placing an order
What Our Customers Say
Dreambot3D FDM 3D printers for your choice
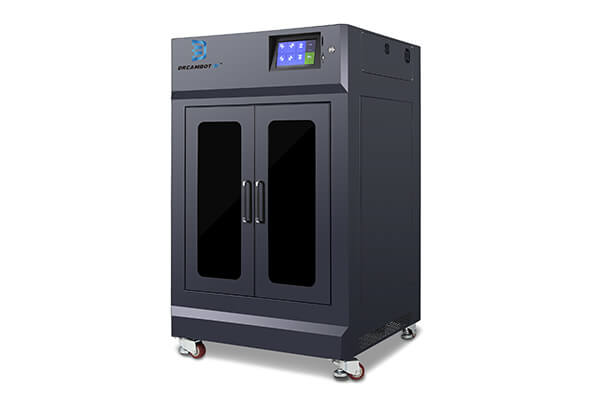

L-400 FDM 3D Printer
The L-400 printer has a printing volume of 400*400*400mm used for small to medium application needs. It is used in manufacturing, medical applications.
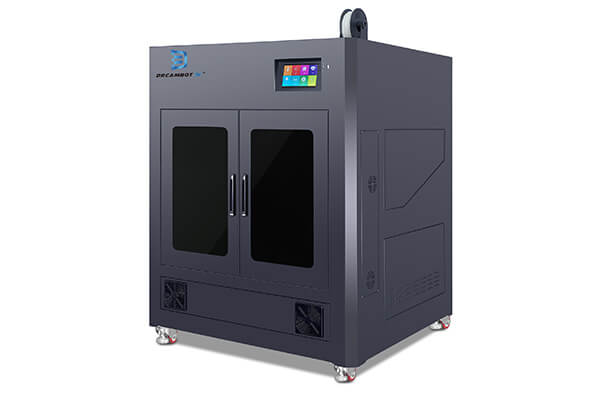

L-800 FDM 3D Printer
The L-800 printer is to print objects of 800*800*800mm mostly found in industrial applications. It is suitable for printing objects with complex geometries.
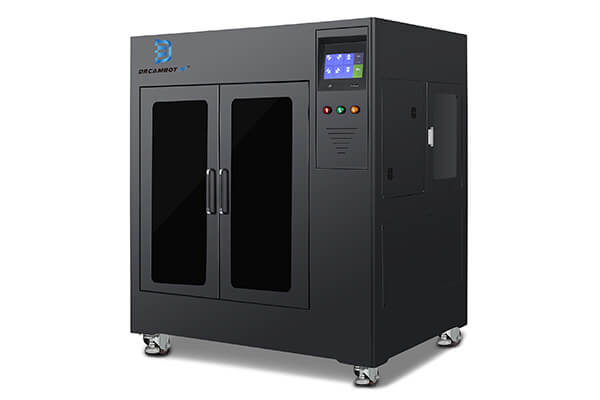

L-1000 FDM 3D Printer
The L-100 printer s used for extremely large applications such as aerospace, construction, automotive, etc, because of its large printing size of 1000*1000*1000mm.
buying guide
3D printer filament is the feeder stock for designing and producing objects such as prosthetic arms and table top gaming parts by armatures and professionals alike. Mainly available in different types of plastic, 3D printer filament can make various products, depending on its manufacturer, physical, and chemical properties.
This buying guide will give you an in-depth understanding of the standard filament used in FDM 3D printers, their properties, benefits, and the resultant everyday products. It would help if you took the time to read through this piece to be in a position to make the right buying decisions when you go searching for the suitable filament used in an FDM 3D printer.
Common Filament Used in FDM 3D Printer
The FDM (fused deposition modeling) printer is one of the two most standard 3D printers on the global market today. It utilizes a printing method that involves the gradual fusing together of materials in a pattern to form objects. The printer melts the filament and pushes the material out, depositing it on top of the already-forming model one layer at a time. Available in different types, the printing material melts at different temperatures, helping you create objects at different speeds.
FDM printing is possible using different materials, primarily thermoplastics, pastes, chocolates, wood-infused thermoplastics, and metal-infused thermoplastics. However, not all of these materials are useful when doing 3D printing professionally. Without regard to the specific 3D printer filament manufacturer, this chapter discusses the different materials suitable for efficient FDM 3D printing.
1.1 PLA Filament
PLA or polylactic acid is a biodegradable vegetable-based plastic material featuring cornstarch as its primary raw material. It is one of the best thermoplastics for making 3D printer filament for FDM printers. Thanks to its base raw material, PLA filament is prevalent in manufacturing additives via the FDM technology.
Every 3D printer filament manufacturer presents PLA filament in a spool with a wire, which feeds into the extruder head, melted, and deposited continuously on the platform to produce the printed object. Even though naturally translucent, it may come in colored filament for making objects in various colors.
When cooling, PLA may shrink less than materials such as ABS, giving it the geometric stability for making different types of objects. It is the best polycarbonate filament for large-scale printing of industrial and professional parts, measuring 1m x 1m x 1m.
Besides, PLA filament from most manufacturers is affordable. However, the model’s total cost will depend on its size, volume, and whether it is wholly or partially solid. Even though PLA filament models can deteriorate when exposed to water, they come in various colors for effective FDM printing.
1.2 ABS Filament
Apart from PLA, ABS (acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) filament is one of the most popular thermoplastics in 3D printing. It is excellent for FDM 3D printing of household, personal, and industrial items. ABS contains polybutadiene-based elastomers, making it flexible and shock-resistant. Even though having a lower tensile strength than PLA, ABS filament for 3D printer application has a higher glass transition temperature and density. Besides, ABS isn’t biodegradable, is reusable, and welded together through chemical processes.
ABS is the best 3D printing material for various applications, especially those requiring thermal stability, machinability, ductility, and strength. It is excellent for printing sports equipment, automotive parts, medical machinery parts, electronic or electrical enclosures, and toys. However, it shrinks when drying, necessitating the printing platform’s heating to stop the model from warping.
Furthermore, FDM 3D printing with ABS filament should happen in a closed chamber to prevent the emission of harmful particles. Recent reports indicate that melting ABS material could result in toxic fumes, which could harm anyone within the vicinity.
Regardless of the 3D printer filament manufacturer, the materials always come out white with a yellowish color due to oxidation, limiting the color variety of models. For a more colorful printed object, you can paint the material whichever way you like.
1.3 PC Filament
PC (polycarbonate) filament is a dominant material with cross-industry applications like printing safety glasses, DVDs, bulletproof glass, and riot shields. Thanks to its icy, translucent prints, it is incredibly tough, heat resistant, and with high optical clarity. Even though it produces vital replacement parts for machines, PC filament presents printing problems, which you can solve by strict adherence to the settings recommended by the manufacturer.
Printing with PC filament should occur in an enclosure or controlled environment to prevent exposure to extremely high temperatures and fumes. At the same time, it is crucial to turn off part cooling for proper interlayer adhesion. Given PC’s tendency to ooze during the printing process, it is necessary to tune the retraction settings for 10 mm or less retraction distance to prevent jamming.
To get the best polycarbonate filament for 3D printing, you need to store the PC in controlled, low-humidity environments. That’s because PC is extraordinarily hygroscopic and absorbs lots of moisture from the air. Therefore, use airtight containers to store PC filament. If the PC filament absorbs moisture before use, then drying it in a commercial filament dryer, food dehydrator, or oven would bring it back to its optimal printing quality.
1.4 TPU Filament
The versatile, flexible, abrasion-resistant TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane) filament exists in different blends for use in various consumer and industrial applications. Users can choose between polyether polyurethane, polyester polyurethane, or a combination of the two depending on the needs they wish to satisfy. Due to its ability to resist chemicals, oil, wearing, and abrasion, TPU 3D printer filament is excellent for use in the automotive industry.
One of the significant advantages of TPU filament is its resistance to low temperatures, preventing it from becoming brittle and improving the ease with which you can work with it. Besides, it is flexible, easy to print, and remains elastic at lower ambient temperatures. TPU also provides incredible interlayer adhesion free from delamination and curling throughout the 3D printing process.
A 3D printer filament manufacturer may use a different blend of polymers, determining the hardness of TPU and the extruder temperature, which lies anywhere between 220 and 250 degrees. Even though TPU printing doesn’t require heating of the build platform, it requires much more energy than most other filaments for FDM printers. Its flexibility makes it more challenging to use than the rest of the 3D printer filament types, which means being careful when choosing a high-quality 3D printing filament manufacturer.
1.5 Nylon Filament
Nylon is one of the most versatile 3D printing materials, great for making cable ties, screws, bolts, nuts, and plastic gears. It is a rigid, semi-flexible material with incredible resistance against abrasion, heat, and fatigue. For successful 3D printing, nylon filament should have anything between 220 and 250 degrees Celsius. The nylon filament 1.75mm most commonly available in the market worldwide since it works with many 3D printer types.
However, the hygroscopic nature of nylon filament for 3D printer applications makes it absorb too much moisture from the air, rendering it virtually unusable afterward. You can avoid print quality issues resulting from too much moisture absorption by storing nylon filament in a dry, airtight container. A filament with exposure to moisture needs drying before use in 3D printing.
The printer bed needs heating to anything between 70 and 90 degrees Celsius for successful nylon 3D printing. In most cases, a glue stick build surface would firmly hold the model in place regardless of the 3D printer filament manufacturer. Exposure to cooler ambient temperature tends to cause warping in nylon printed objects, necessitating the use of a controlled environment like a heated chamber or enclosure with a 45 degrees Celsius ambiance.
1.6 Carbon Fiber Filament
Carbon fiber filament is a composite material derived from infusing carbon fiber fragments into a polymer base. Even though not as tough as pure carbon fiber, the filament has improved strength compared to the base polymer material – nylon, ABS, or PLA – giving the end product more excellent dimensional stability free of shrinking or warping. Its extruder temperature largely depends on the base polymer material used to mix the carbon fiber particles.
For example, carbon fiber filament based on nylon prevents the warping and shrinking that occurs when nylon gets into contact with cooler air. Using it eliminates the need for 3D printing in a controlled environment with a constant temperature.
The amount of carbon fiber in the mixture may vary depending on the 3D printer filament manufacturer, making the material behave differently during the printing process. However, one constant behavior is carbon fiber’s heat resistance, which prevents it from melting when heated. Therefore, these particles may lead to continuous extrusion nozzle clogging, making printing rather frustrating. An adjustment of the retraction settings can help avoid clogs caused by carbon fiber particles.
Furthermore, carbon fiber particles are highly abrasive and may gradually wear down the brass extrusion nozzles. You can prevent that by acquiring a printer with hardened steel nozzles geared for printing composite materials like carbon fiber filament. To get consistent results from this material, it is also necessary to reduce the print speed significantly.
Application of 3D Printer Filament
To better explain the importance of 3D printer filament, let look at some of the industries where their usage plays an important role in their everyday activity.
2.1 Industrial R&D
The use of 3D printers for industrial R&D has brought about ease of design, efficient production process, and time-saving development procedures to experts in numerous industries. Ranging from hobbyist designing molds for the production of jewelry to experts in aerospace and medical printing, 3D printers have taken a front role.
Nonetheless, there is a lot of confusion about choosing the right 3D printer filament for industrial R&D. Every 3D filament has a different set of properties, which make it suitable for certain applications while unsuitable for others. For example, concept prototypes are used only for display purpose and not for functional testing so using a material which is simple to print with is the correct choice instead of going for a strong material which is difficult to print with.
When it comes to choosing the right 3D printer filament for industrial R&D, you need to put a lot of factors into consideration. Ease of use, strength, durability, flexibility, heat resistance, aesthetics, and complexity of print are amongst the many factors you have taken into consideration.
2.2 Mold
The majority of plastic products in the world today are manufactured by injection molding. However, fabricating molds can be prohibitively expensive and time-consuming. Fortunately, molds don’t always need to be machined out of metal—they can be 3D printed.
All you need to 3D print a mold is the right 3D printer filament. There are multiple 3D printer filament available for printing the mold. Note that the durability and efficiency of the mold making industry or the mold you make use of daily in your production line is dependent on the 3D printer filament you are making use of.
If you’re frustrated that traditional 3D printing necessitates creating one object at a time, 3D printed molds will help you enormously. Although you do have to create one mold at a time, once you’ve got your set ready, with a preffered 3D printer filament, you can use them all at once, and mass manufacture your objects in batches that will speed your production nicely.
2.3 Aerospace
Due to the typically short runs of aircraft parts, the aerospace industry uses 3D printers for industrial R&D for a great deal of its production. The technology can produce intricate parts that are more resilient and lightweight compared to those made using traditional techniques, which is an obvious bonus.
Generally speaking, the Aerospace industry was one of the earliest adopters of 3D printing technology, with initial use recorded back in the late 1980s. Nowadays, it is still considered the industry which has the highest rate of adoption of 3D printing technologies.
However, just like in every other industry, the importance of 3D printer filament in the aerospace industry cannot be undermined. To enjoy an efficient and well detailed aerospace printing process, its essential you make use of 3D printer filaments from reputable manufacturers.
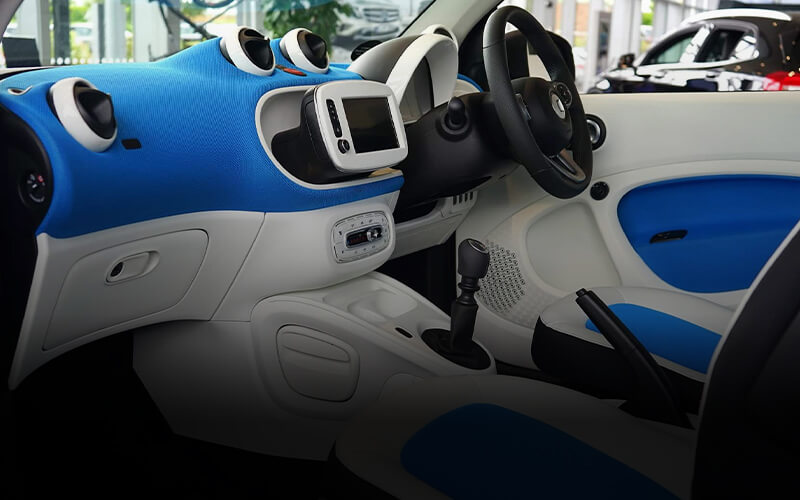
2.4 Car Parts
The 3D printing technology has given rise to spectacular achievements in the automotive industry, starting from the possibility of fast prototyping, through a more and more widespread production of final car parts, and ending with 3D manufacturing of nearly the whole cars. Nobody should be surprised with a growing interest in 3D printers for industrial R&D on the part of large concerns, such as Mitsubishi Chemical or BASF, which see a serious and profitable business in using FDM printing technology in the automotive sector.
The automotive sector has liked rapid prototyping 3D printing and has been using its opportunities on a daily basis more and more often. Designers and engineers open to innovation implement bold ideas with the use of the technology, thus, extending the pallet of engineering benefits and optimizing the manufacturing processes.
And since it’s no surprise that you can’t print car parts without the right 3D printer filament, its important you have it at the back of your mind that you can’t run an efficient car parts production line if you don’t have the right 3D printer filament manufacturer in your corner. Get in touch today, Dreambot can help you streamline an efficient filament purchasing process for your car parts production line.
2.5 Medical
3D printers for industrial R&D has many functions in a variety of industries; however, in the medical field, it has four main applications. Rapid prototyping 3D printing could be used to replace human organ transplants, speed up surgical procedures, produce cheaper versions of required surgical tools, and improve the lives of those reliant on prosthetic limbs.
Additive manufacturing, otherwise known as 3D printing, was first developed in the 1980s. It involves taking a digital model or blueprint of the subject that is then printed in successive layers of appropriate material to create a new version of the subject.
And from its inception till date, reliability and dominance have been hugely dependent on 3D printer filaments. There are multiple 3D printer filament suitable for experts and professionals in the aerospace industry, to ensure you are making use of the right filament in your production line, please get in touch today.
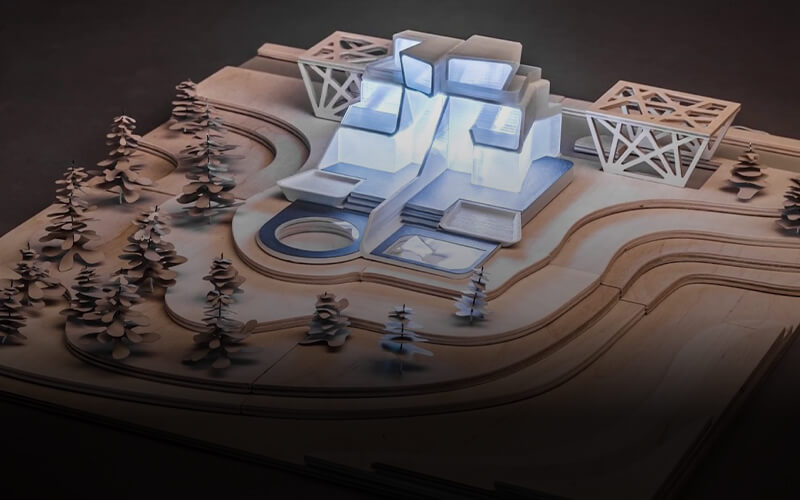
2.6 Architectural Model
Architecture is one of the few industries 3D printing has reshaped allowing architectures to easily view their archetype before construction, however, complex the model may seem, the 3D printer will easily create it, just think of your ideas or thoughts coming alive, more tangible. A 3D printed model allows architects to share their ideas with their clients and colleagues visually, giving both teams a better understanding of the proposed project.
With 3D printing, designers are now able to print objects out of materials like concrete giving them less time for production, this is because the printers are fast, fast enough that some are capable of constructing 600–800 square feet of property in 24hours. Miraculous, right? But that doesn’t mean 3D printing will eliminate architects and designers. With 3D printing blueprints, there are tons of opportunities for designers and architects to create exclusive models for their clients.
Imagine printing accessories like floorboards, an internal wall, and many more into the building, you can easily achieve this with 3D printing, poised to make work easier for architects.
For the best and accurate results for architectural models, you’ll need the right tools, inquire from a 3D Printer Filament Manufacturer.
2.7 Mannequin
3D printing will save you a lot of time when printing mannequins. When it comes to custom-made mannequins it takes a significant amount of time for production, sure there are merits for handmade mannequins, but waiting for weeks or maybe months to produce a life-size mannequin can be a non – starter for some. Now, with a 3D printer it saves you tons of time, a 3D printer can produce a mannequin in just a matter of hours, or days, enabling you to meet a short deadline and giving your client the exact specifications they desire.
With no trouble at all designers can scan any character and print them out in any pose they desire, you may also re-version within the existing one. To meet accuracy or best results you’ll need to use the best filament, the PC filament 1.75 or the PC 3D printer filament would be the best choice for printing mannequins, it is fast and efficient, and easily acquired from a 3D Printer Filament Manufacturer. You could easily say 3D printed mannequins are the future, as a matter of fact, the future is now. Design your own mannequin from scratch or based on an image of your own, move with the future.
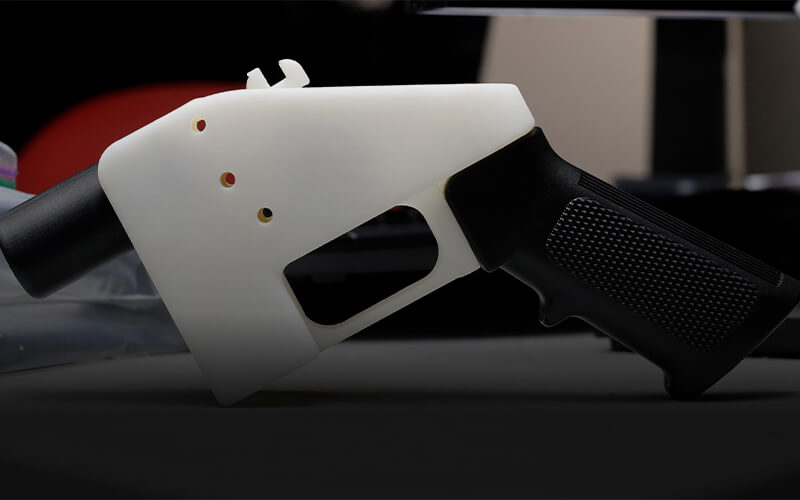
2.8 Guns
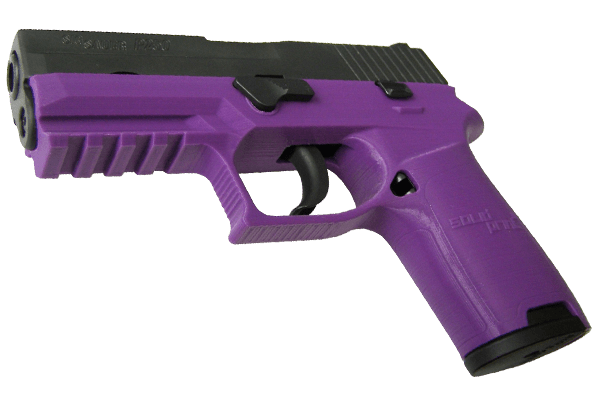
3D printers are slowly gaining widespread fame and altering the way many items are being manufactured. But when it comes to 3D printed guns it varies a lot, you will require certain parts to add to your model, oftentimes are metal. Do not underestimate the power of a 3D printer as these printed guns do work and can fire hundreds of rounds, in other words they can be lethal if built properly, but if not, it might blow up on your hand when shooting, so best to visit a 3D Printer Filament Manufacturer to guide you through some of the basics and direct you on which filament to use if you’ve never printed a gun before. For experts, one of the strongest 3D printing filaments you can use is Nylon filament 1.75, it may be slightly more expensive but this is due to its toughness.
But are 3D printed guns legal? In some cases it is legal, the federal law will tolerate the manufacture of unlicensed firearms, including one made from a 3D printer so long as you don’t include metallic elements without a proper background check from the authorities.
2.9 Anime Figure
Why shop for anime figures when you can make your very own? Design it however you want, your own special action figure or doll. While you can’t possibly buy a 3D printer for the sole purpose of printing an anime figure, it’s still very fun creating your own custom anime figure from scratch, or a scanned image of the proposed model, that is if you have a 3D printer. To achieve fine details and accuracy, consider a 3D Printer Filament Manufacturer to always help out whenever you’re stuck and can’t get out.
If you love action figures or anime figures you can create any print you want, from pokemon to dragon ball, print all these at your own comfort, let us give our kids a chance to drift off to their favorite worlds. You’ll want your action figure durable, which means you’ll want a filament that is printable, durable, and won’t break easily on impact, nylon is a very strong printing filament and a 3D Printer for Nylon should serve well and produce great results.
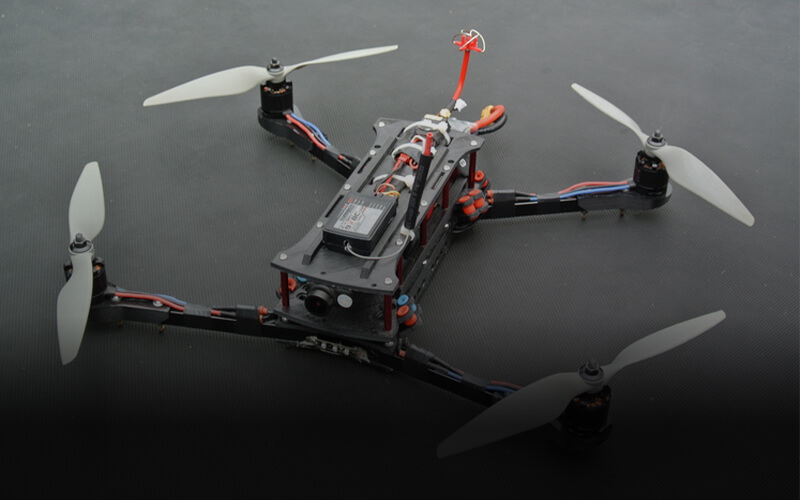
2.10 Drone
3D printing is no guest to air travel and can be a very useful tool for your aeronautic project, add parts to your 3D printed drone, upgrade or build one from scratch, but to power your drone you will need non-printed parts like the batteries. 3D printing makes your pilot training and everyday mistakes easier to manage as you’ll have an infinite supply of parts, you can easily print a part and repair it anytime it breaks, even though certain companies and retailers guarantee fast delivery it surely can’t surpass printing one at your comfort, not to forget satisfying.
The number of drones being manufactured on a regular basis is always increasing, but finding the perfect drone that suits your needs may be a task, but with 3D printers, you can create and design your drone to meet your requirements and save tons of money (assuming you already own a 3D printer and a filament). To build strong parts you will need to consider the strongest filament you can use. In particular nylon, the Nylon 3D filament should be ideal to print a drone or certain parts as it can build durable parts if printed properly, excluding all electrical parts.
How 3D Printing Filament is Applied to 3D Printers
Choosing a 3D printing filament from a notable 3D printing filament manufacturer may come with its confusion as every known material or filament has its pros and cons and it’s all dependent on its application and the type of printing technology in use. The FDM 3D printing technology is most common while dealing with 3D printing filaments.
3.1, Printer that matches filament FDM 3D printer
Another printing technology that matches the filament FDM 3D printing is the SLA (stereolithography) and by comparison, FDM and SLA printers have complimentary and similar features and are most times used side by side by many businesses with its low-cost rapid prototyping and high-quality yield. Both FDM and SLA 3D printing is commonly used in manufacturing to create jigs, fixtures, and another tooling.
SLA 3D printing is ideal for detailed concept models and functional prototypes. 3D printers that work on FDM tech consist of the printer platform, a nozzle or printer head, and the raw material in the form of a filament.
As it is computer controlled, the machine head moves in a dual dimensional way, forming layers of the part under creation. Custom FDM printers for modeling small parts and restructuring mannequins are used by hobbyists, while manufacturers including 3D printer filament manufacturers also use them for creating materials that are heat resistant and can withstand intense functional testing.
3.2, Printing principle of FDM 3D printer
Without the need for assembly and with a provision of portable modeling and manufacturing, there’s a reduction of costs associated with 3D printing, an increased ability to print on demand, deliver precise physical replication of designs, and meeting the modeling, printing, and finishing principles.
As the most popular and affordable 3D printing tech use, the FDM printing system is also known as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) or Material extrusion additive manufacturing technique, use material extrusion to print items, where a feedstock material is pushed through an extruder head, forced out of a heated nozzle onto a flatbed, with the feedstock material coming in a thermoplastic filament form wound unto a spool forming coil. The raw material is extruded as a thin filament through the heated nozzle as the FDM printer begins printing. It is then deposited at the bottom of the printer platform and solidifies forming a layer. Fusion of layers following a repeat of this extrusion occurs thereby building the object in view bottom-up layer by layer.
Most FDM printers first print the outer edges, the interior edges next, and lastly the interior of the layer as either a solid layer or as a fill-in matrix.
Possibilities of ‘overhangs’ drooping unless given some form of support is avoided as FDM printers come with a support mechanism known as struts which are usually of the same material as the object and these get printed alongside the object. They are removed once the build is complete.
Some printers come with multiple extrusion nozzles or a ‘second’ extruder for specifically depositing soluble thermoplastic struts when there is a need to prevent the overhangs from drooping. These struts may be of a different composition than the thermoplastic used for the 3D models which are later dissolved by an appropriate solvent. So have you been searching for an efficient 3Dprinting filament manufacturer? Get in touch with our Customer Representatives. We have what you need.
3.3, Basic Requirements of FDM 3D Printing Materials
Any thermoplastic can be used as a raw material for FDM printing.
More popular choices due to commerciality include Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), Polylactic acid (PLA), polycarbonates and carbon fibers, polystyrene, nylon, and thermoplastic urethane.
Ease of use, durability, flexibility, increased strength, heat resistance, the complexity of prints, and aesthetics are a few of the factors to be considered while selecting your material for 3D printing.
As a leading 3D printer filaments manufacturer, Dreambot provides bio-compatible and damp-resistant raw materials. With a wide range of PLA, ABS, Nylon, and carbon fibers, stable quality and high precision is guaranteed. Some of the filaments available in our catalog and their basic requirement include,
- PLA
PLA, a biodegradable thermoplastic material is derived from renewable resources like starch making it different from other used plastics gotten from distillation or polymerization of non-renewable resources. Available in varying colors and blends, PLA materials have become very common especially with the rise in the availability of custom FDM printers. It is also seen as the best aesthetic material for use in prototyping.
- ABS
ABS can melt and cool without changes to its chemical properties. It is a strong, tough, and durable thermoplastic polymer with good heat, pressure, and stress-resistant qualities. Unlike PLA, under the right temperature and setting, the breaking of an ABS 3D printing material rarely occurs as it rather distorts and bends when a strain of its filament is moved.
Surfaces with ABS 3D filament material can be processed with acetone; glue parts or filed as well as easily painted with acrylic colors. While dealing with ABS 3D printing filament materials, it’s important to avoid exposure to very high temperatures of up to 400°C, as this decomposes the material into possible carcinogenic substances like butadiene.
- Nylon
Nylon or polyamide is known for its flexibility amidst toughness. Temperature ranges while working with Nylon filaments vary from as low as 220°C to as high as 250°C.
Though nylon filaments may be hygroscopic and prone to warping, they have no unpleasant odor while printing and have a high impact and good abrasion resistance.
- Carbon Fibers
Carbon fibers are a product of the infusion of carbon fiber in a polymer base, which can be of a different 3D printing material including Nylon, PLA, and ABS.
They serve as cheaper and tougher alternatives to more expensive and demanding materials like polycarbonates thereby improving dimensional stability, increased rigidity while avoiding shrinking and warping. Note that clogging of the nozzles can occur following the use of these infused carbon fibers which act as abrasive agents and aren’t melted during extrusion thereby requiring special nozzles like hardened steel instead of brass.
When in search of your quality carbon 3D printer filaments or other materials, it is invaluably important to choose the right 3D printer filament manufacturer as well as the right product.
Questions like how long has the 3D printer filament manufacturer been in business?
What is their customer feedback and brand identity like and are they regarded as top professionals?
What is the efficiency rate of their products such as the ABS 3D printing material or carbon Fiber filament material for 3D printing?
And a host of other questions you may be having while carrying out your brand review before purchasing can comfortably be answered by us. Contact our support representatives today and get a review of our catalogs.
How to Choose a High-Quality 3D Printing Filament Manufacturer
You now know all there is to know about filaments and their basic requirements. Now to the big question, how do you choose the right 3D printing filament manufacturer?
4.1 Check the Brand Reputation
With the advancement of technology, there are always overwhelming choices available when it comes to equipment. This also applies to 3D printing filaments. When buying filaments, you need to determine if the 3D printer filament manufacturer meets your expectation, budget, and the kind of parts you hope to print.
With new products and types of materials flooding the market, you need to do a lot of research to make well-informed decisions. In order to get a good brand, there are certain things to consider about the 3D printer filament manufacturer. It would be best to look out for buying ratings and reviews from users, reviews from professionals in the field, and a brand that offers a good customer support system.
It is advisable to also look at how many years the 3D printer filament manufacturer has been in the market. There are a lot of new filament manufacturers springing into the industry daily. Some of these companies have little or no experience in the industry. So, it is necessary to consider how long a 3D printer filament manufacturer has been in the market; their experience in the industry might be helpful.
It can also be helpful to look at manufacturers that bring innovation and keep in touch with modern technology. The 3D printing industry has undergone a lot of innovation since its foundation. So, it would not be nice to go for a filament manufacturer who has done nothing to improve its quality in line with modern technology.
4.2 Go For Flexibility
If you are hoping to print objects that experience a lot of wear, stretching, bending, and compression, you have to choose 3D printing filament materials that are flexible. Filaments like Nylon, TPU, TPE, and TPC are the best filament materials with flexibility.
These filament materials are plastics with rubber-like qualities, and this makes them very flexible and durable. These filament materials are soft and stretchable, and they can withstand any physical punishment. They retain elasticity in the cold, and they have a high resistance to chemical and UV exposure. These filaments are best used for printing automotive parts, medical supplies, and household appliances.
Nylon filament belongs to synthetic polymers and is one of the most widely used in industrial applications and professional 3D printing. It ranks as the number one because of three outstanding qualities; flexibility, strength, and durability.
Nylon filaments have a high impact and abrasion resistance, making them the ideal filaments for printing durable parts. This filament can be used to create tools, mechanical parts (buckles, hinges, and gears), and functional prototypes.
One of the cons of nylon filaments that you should know is that they are hygroscopic. This means that they quickly absorb moisture from the surrounding environment. This can affect the quality and outcome of your work; printing nylon filaments after they have absorbed moisture can cause print quality issues. Another type of filament similar to nylon filament is Polycarbonate filament, also known as PC filament.
Polycarbonate is one of the strongest 3D printer materials, and it is durable and resistant to heat and physical impact. PC filament is moderately flexible though it is not as flexible as nylon. It is used for commercial items like electronic display screens, scuba masks, and bulletproof glass.
Polycarbonate is sometimes reinforced with carbon fiber to add strength to it, and this combination gives it the name PC carbon fiber filament. PC filament has the same hygroscopic qualities as nylon and absorbs moisture when exposed. So, it is better to store it in an airtight environment to get quality printing. Nylon filaments and PC filaments offer good flexibility and durability best suited in industrial application and professional printing.
4.3 Attention To Details
One of the frustrations of 3D printing, among many others, is using the wrong type of filament for your job. The quality of the filaments you use will determine the quality of your final printed object.
In order to get good quality printed objects, you need to consider a 3D printing filament manufacturer that produces the best filament materials. It would be best if you also chose filaments that have compatibility with your 3D printer. If the filament materials are not compatible, your printer will not give you satisfying results.
The 3D printer filament manufacturer you chose should have a track record with good reviews from users and experts in the 3D printing industry. Also, it is essential to pay attention to the material used for your 3D printing nozzle.
Your printing nozzle affects the choice of the filament type you use. 3D printers with brass nozzles are best used to print materials like nylon, ABS, and PLA. If you use filament materials like carbon fiber on your brass nozzle, you will notice some wear and tear on your printer’s nozzle.
When using a carbon fiber filament, it is advisable to use harder materials like stainless steel and tempered steel for your printer’s nozzle. This will significantly reduce the wear and tear of your printing nozzle. The choice of filament you choose will also depend on what you wish to produce, and it could be mechanical or aesthetic products.
If you are hoping to print flexible or semi-rigid objects and parts, you should consider using nylon filaments. If you want an impact-resistant object, then you could consider using polycarbonate. First of all, it is always important to know what your printed object will be used for before you choose the type of filament. Paying attention to these little details will save you a lot of cost and time.
4.4 Put Safety First
We can get carried away by the excellent price and discounts that a particular 3D printer filament manufacturer offers. This can make you forget the most important thing: the quality and safety of the filament materials. The whole idea of using a 3D printer is to provide a safe printing environment and a smooth experience, thereby saving costs.
You should not purchase a 3D printing filament if you have not first tested its productivity and outcome. 3D printing filaments can be toxic, especially when melted at very high temperatures. The lower the temperature used, the less toxic the 3D printing filament will be. 3D printing involves thermal decomposition when the filament is melted at high temperatures.
This melting produces toxic fumes and volatile compounds, which pose health issues and concerns. It would help if you took some safety precautions to avoid the toxicity produced from the melting of these filaments. It is highly recommended that you print in a space with a good ventilation system installed.
Do not use your 3D machines and materials in the same room that you sleep in. Also, you can print in an open space; this helps to expel the fumes away and filter the air. It is necessary to research the types of 3D printing filaments that you are using to follow all the manufacturer’s safety precautions.
If you are printing an object used for food items like cutleries, it is advisable to use food-safe plastic filaments. This will help you avoid food poisoning; always refer to the instructions stated by the 3D printing filament manufacturer.
4.5 Select The Most Cost-Effective
When we buy products, we look at the famous brands, and we sometimes think that the costliest filament brands are the best. Well, you will not be wrong because some 3D printer filament brands have lived up to the expectations. And their high prices are worth it because they sell quality materials.
Some 3D printer filament brands do not live up to their reputation; they have dropped the quality of their products. These brands might sell costly filament materials which might not be of good quality. This does not also mean that choosing the cheapest brand will guarantee you suitable 3D printer filament materials.
So, before buying any filament materials, it is good to do background research about the 3D printer filament manufacturer. Make sure that you are getting quality for your money; buying the best filament materials will save you from a lot of stress and disappointments.
If the product has quality, but it is expensive, it is better to go for it than going for something cheaper, which might give you a less quality outcome or cause more problems for you in the long run. Whether cheap or costly, endeavor to buy a 3D printer filament that suits your 3D printer, helps you achieve your goal, and delivers a quality outcome.
4.6 Why Choose Dreambot3D Filament
When choosing a 3D printer filament manufacturer, choosing a reliable company with experience and a good track record is necessary. At Dreambot3D, we manufacture some of the highest quality filament materials in the industry, and we are regarded among the top 10 3D printing service providers.
We cater to your 3D printer filament needs by offering high resolution and top-notch printing filaments. We specialize in Nylon 3D printing materials for industrial R&D in medical printing, dental printing, aerospace, automotive, and tech. We are capable of handling your various needs.
We pay attention to details, and our priority is to deliver quality 3D printer filament materials and services. We provide fast and instant quote and purchase options. We are willing and ready to attend to your 3D printer filament needs.
FAQs
What is the best filament to use for 3D printing?
Polylactic acid, well known as PLA, is the most preferred 3D filament type from 3D Printer Filament Manufacturer. It is a thermostatic polymer derived from renewable sources such as corn starch and sugarcane. It is a biodegradable product usually broken down in three to six months and therefore environmentally friendly. It is primarily used as a filament in Filament Deposition Modeling (FDM). PLA filament is available in various colors and blends, making innovative PLA-based materials the order of the day in the market. Inside the Filament Deposition Modeling 3D printing sphere, the polylactic acid filament is considered an anesthetic material that is the best for photocopying.
What type of filaments are used to 3D print?
- Nylon
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
- Carbon fiber reinforced filaments.
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)
- Flexible polyester (FPE)
- Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA)
- Polyethylene terephthalate with glycol (PETG)
- Acrylonitrile styrene acrylate (ASA)
- Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE)
- Polyoxymethylene (POM)
- Polypropylene (PP)
Can 3D printers use any filament?
It is not always as some plastic needs a high-temperature nozzle and heated bed, and for the cheap printers, they cannot reach temperatures. Most filaments from Dreambolt 3D printer Filament manufacturer come in diameters of 1.73mm. However, some 3D printers can use up to 3mm filament, and hence cheap printers cannot handle such. However, most common filaments from 3D Printer Filament Manufacturer are made from PLA, and therefore, any filament-based 3D printer can manage that because the temperatures required are very modest.
How strong are 3D printed parts?
3D parts are powerful only when made from specialized filaments such as ABS, PLA, and PETG. They are strong enough to make plastic items that are resistant to heat and many other impacts. These parts are made much more robust by bumping up the infill density, improving the wall thickness, and increasing the walls.
What is the most durable 3D printing filament?
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is the King of this. Due to its nature of plastic, ABS is easy to print with from a hot end. It prints at 210-250ᴼ C with a heated bed at 80ᴼ C or more.
How durable are 3D printed parts?
Durability depends on the material used by 3D Printer Filament Manufacturer, print technology (FDM, SLA, SLS, etc.), desired usage, and the environment. Narrowing down further, temperature, pressure, budget, size load to be handled can also be considered.
Is 3D printing ABS toxic?
ABS releases toxic fumes known as Volatile Organic Carbon (VOCs), which may be toxic, especially to young users. Furthermore, everyone knows that the unpleasant odor produced by ABS cannot be healthy to breathe in.ABS also produces nanoparticles that can be absorbed in the lungs causing various lung pathologies and the skin’s epidermis.
Which 3D printing material is the strongest?
Polycarbonate is the order of the day for the strongest 3D printing material produced by 3D Printer Filament Manufacturer. Having high tensile strength, PC yields high-strength parts when printed correctly and with an all-metal hot end together with an enclosure.
Can 3D printers print carbon fiber?
Typical carbon fiber has chains of 5-10 micrometers; however, short carbon chains of less than one millimeter long are used for 3D printing. These carbon fibers are combined with a thermoplastic that acts as a base material. Materials used include PLA, Nylon, ABS, Polycarbonate etc.
What is carbon fiber 3D filament?
It is a composite carbon material formed by infusing chains of carbon fiber in a polymer base such as Polylactic acid (PLA), Acrylonitrile Butadiene styrene (ABS), PETG, Nylon, and many others. They consist of short particles of around 0.01mm in diameter, which are enough for improving the strength of printed parts. This increased strength helps in avoiding warping and shrinking.
What is the strongest filament for 3D printing?
The strongest 3D printer filament you can buy is polycarbonate filament. Its mechanical structure is unlike many others, where strength tests have shown the excellent resilience and strength of this filament. Polycarbonate is widely used for engineering and has a PSI of 9,800 compared to PLA’s 7,250.
Is 3D printed carbon fiber strong?
Yes, 3D printed carbon fibre are strong. Carbon fiber makes the 3D printing material stronger and sturdier. The prints produced using this material are also lighter and are more stable in terms of its dimensions. The fibers aid in preventing any parts from shrinking as the print cools down.
Is ABS good for 3D printing?
ABS is a low-cost material, great for printing tough and durable parts that can withstand high temperatures. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) has a long history in the 3D printing world. This material was one of the first plastics to be used with industrial 3D printers. Many years later, ABS is still a very popular material thanks to its low cost and good mechanical properties.
Is ABS filament safe to print with?
Yes, ABS filaments are safe to print with. ABS can melt and cool without changes to its chemical properties. It is a strong, tough, and durable thermoplastic polymer with good heat, pressure, and stress-resistant qualities. Unlike PLA, under the right temperature and setting, the breaking of an ABS 3D printing material rarely occurs as it rather distorts and bends when a strain of its filament is moved.
How long does 3D printed ABS last?
ABS is said to last around 10 years, but I’m sure it can last longer when it is stored as normal, then dried before 3D printing. If the filament absorbs too much moisture from the air, it may degrade, bubble, or simply produce some horrible prints that you won’t be happy with.
What is ABS filament good for?
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) boasts excellent mechanical properties, ideal for objects that require toughness and durability. One drawback many experience is that ABS can be trickier to print than PLA, with parts sometimes warping during the printing process. However, there are ways to reduce this.
How strong is 3D printed plastic?
3D printed parts are very strong, especially when using specialized filament like PEEK or Polycarbonate, which is used for bullet-proof glass and riot shields. Infill density, wall thickness and print orientation can be adjusted to increase strength. You might also want to keep in mind that 3D printed parts are only as strong as the materials they are made with.
Can nylon be used in 3D printing?
Yes, nylon can be used in 3D printing. Nylon is an incredibly strong and durable material for 3D printing. It is abrasion resistant, heat resistant, and has a low friction coefficient. It is flexible when printed thin, solid when printed thick, and offers outstanding dimensional stability during the print process. Nylon will not stick to glass or metal build plates, has low odour, and it prints with a finish that is akin to smooth sandpaper. It is commonly available in transparent and black.
Is nylon filament toxic?
Yes. It can be alarming as it is a risk to your health. Harmful fumes usually originate from certain thermoplastic and plastic filaments mainly like ABS, Nylon and PETG. However, Nylon filaments are plastic in nature, produce no noticeable smell but the fumes are still toxic as they emit gaseous compounds.
What is nylon filament used for?
Nylon is a durable, resilient synthetic polymer that is highly absorbent. It is used both for material extrusion and powder bed fusion 3D technologies, which makes it one of the most popular 3D filaments.
How strong is 3D printed nylon?
Nylon is more robust than ABS 3D printing material. Its strength makes it suitable for use in producing parts of commercially viable products. With an ordered molecular structure, hydrogen bonds, and long strands, nylon has a higher tensile strength than most other materials. Moreover, nylon filament for 3D printers comes with a low friction coefficient, making it great for mechanical parts such as pulleys, bearings, threads, and gears. Thanks to its enduring strength, nylon can stretch and yet regain its initial shape quickly. It is hard to damage or tear and is durable. It is excellent for thin-walled 3D-printed parts capable of resisting wear and tear due to friction. Even though having similar mechanical properties to ABS, nylon is better for applications requiring resistance to wear. Notably, nylon withstands heat and won’t melt in a hot car. Conversely, PLA prints tend to melt at the slightest increase in environmental heat. Finally, 3D-printed nylon is impact and heat-resistant. Any 3D printer filament manufacturer would like it because of its unbreakable nature.
How do you smoothen nylon 3D prints?
You can smoothen nylon 3D prints by brushing off any powder grains that might have stuck on the surface. However, that won’t make the surface smooth enough, so you need to sand the surface. Sanding helps even out layer marks and jagged edges, making the object soft to the touch. If you have used white nylon filament, it is now time to add a little color. You may dip the object into a dye bath or applied paint. A dye bath is suitable for a more permanent colored finish. On the other hand, painting the surface gives it a glossy finish that you can’t achieve via a dye bath.
What printers can print nylon?
Printers that can print nylon are those with selective laser slandering (SLS) technology. With SLS technology, the nylon 3D filament should be in powder form. It produces nylon 3D prints in two quality levels, namely PA11 and PA12. However, there is a more advanced technology called multi-jet fusion (MJF). Printers with MJF technology are accurate and fast. MJF printers also save more than 70 percent of the excess powder. Later on, you may reuse the powder to print more models. The only problem is that printing fast with nylon. That’s why SLS printers are the best for plastic filament. Examples of great 3D plastic printers include Pulse XE – Nylon, LulzBot Tat 6, Qidi Tech X-Plus, Ultimaker S5, Dremel Digilab 3D40 Flex, Velleman Vertex 3D K8400, and Pruisa i3 MK3S.
What is nylon filament made of?
Nylon filament features polyamides – a group of rigid semi-crystalline materials. It exists in various forms, including nylon 6, nylon 66, and nylon 12, depending on the 3D printer filament manufacturer. Any of these can go into producing the standard nylon filament 1.75mm. Of these types of materials, nylon-6 and nylon 6-6 are the most common. Two monomers (each with six carbon atoms) make up nylon 6-6. Other components of nylon 6-6 are adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine. On the other hand, nylon-6 closely mimics nylon 6-6. It came about due to scientists trying to develop a material with properties similar to nylon 6-6 without patent violation. A 3D printer filament manufacturer makes Nylon 6 through caprolactam (a material with six carbon atoms) polymerization to give it a unique yet similar structure to nylon 6-6. Finally, nylon 12 features laurolactam or ῳ-aminotauric acid monomers, each with 12 carbon atoms.
What is TPU 3D printer filament?
TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane) 3D printer filament is a durable, flexible rubber-like material used for 3D printing. It is elastic and resistant to oil lubricants, abrasion, and other stresses. The flexible structure of TPU 3D printer filament results from its interchanging hard and soft segments. TPU 3D printer filament exists in three subgroups, namely polyether TPU, polyester TPU, and polycaprolactone TPU. Polyether TPU has outstanding hydrolysis, microbe, and tear resistance, making it great for use underwater. Due to its excellent oil and chemical resistance, polyester TPU is perfect for parts prone to abrasion. A 3D printer filament manufacturer can blend it with other materials to serve various purposes. Lastly, polycaprolactone TPU is a rigid, durable nylon material great for use in seals. That’s because of its hydrolysis resistance and excellent performance in cold conditions.
Can you 3D print TPU?
Yes, you can 3D print TPU using several types of printers. The best are 3D FDM printers which melt and extrude TPU filament to create various kinds of products. A 3D printer filament manufacturer would mostly use TPU to make flexible products like seals, gloves, and cases. TPU is a flexible material that can result in 3D printing difficulties like deformation, nozzle clogging, and jamming. Therefore, it is essential to use the correct settings and calibration to create various products from TPU 3D printer filament. You can 3D print TPU at 245 degrees Celsius or more. The temperature settings depend on the additives in the material and its hardness.
Is TPU filament safe?
Yes, TPU is safe primarily because it produces little or no fumes. Therefore, you can use it when 3D printing in closed rooms and environments. That’s mainly because TPU 3D printing happens in highly controlled environments that don’t produce toxic fumes. Besides, TPU is food-safe and goes into printing objects that go into food manufacturing and packaging.
How fast can I print TPU?
The speed at which you can print TPU doesn’t exceed 30 millimeters per second. That’s because of the difficulty that comes with pushing correct amounts of the filament through the printer. Besides, TPU prints take longer because the primary method is slower. Notably, fused deposition modeling (FDM) runs at an average speed of 15 to 20 millimeters per second. If you print at a higher speed, it would be impossible to get high-quality prints. With 3D printing, it is only possible to increase the speed by raising the temperature. The molten filament moves through the nozzle faster, giving you higher printing speeds. However, that would diminish the level of 3D printing accuracy you get. It is also possible to increase the nylon filament rate by raising the extrusion multiplier. With that, you will raise the 3D printing speed and the accuracy level.
What is PC filament good for?
PC is lightweight, making it ideal for products that need to be clear, strong, resist heat, and light, and is a heavily used filament in engineering applications, as well as 3D printing sunglasses and riot gear.
Can you 3D print with a PC?
Yes, you can 3D print with a PC filament. PC is more durable and flexible than PLA but less so than nylon. It’s harder than ABS, PLA, or PMMA, while also being lighter and less dense than ABS. It’s ability to withstand torsional stress is superior to other thermoplastics, and it’s flexible enough to be machine bendable at room temperature.
How fast can you print polycarbonate?
In general, the lower your printing temperature, the slower your printing speed should be. We’ve found that 30mm/sec while using a polycarbonate filament temperature of at least 265C will produce good results. If you can get a higher temperature out of your extruder, you can experiment with a faster printing speed, say 60mm/sec. However, at the end of the day, slow and steady wins this particular race.
Does PETG shrink more than PLA?
Both PETG and PLA will show a bit of shrinkage while cooled. This shrinkage rate is much less as compared to other filaments. The shrinkage rate of these filaments when cooled ranges between 0.20-0.25%. The shrinkage of PLA is almost neglible, while PETG does show some visible shrinkage, but not as much as ABS. Comparing other filaments, ABS shrink almost 0.7% to 0.8% while Nylon may shrink up to 1.5%.
Is it safe to print polycarbonate?
Yes, its safe to print polycarbonate. Polycarbonate is a thermoplastic that is most prominently known for its incredible strength and impact resistance. The basis of bulletproof glass, polycarbonate is lightweight and exhibits a translucency that is superior to other Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) 3D printing materials.
Does TPU need a cooling fan?
It is recommended to use a cooling fan with TPU. We highly recommend reducing your print speed when 3D printing TPU. This can be frustrating, especially if you have invested in one of the fastest 3D printers around, but it will be far worse having to continuously unclog your 3D printer’s nozzle if you print too quickly.
Do you need a heated bed for TPU?
The general consensus is that the best 3D printing temperature for TPU is around 230C, with a wider range of between 220-250C. Though you do not absolutely have to use a heated bed, it is highly recommended, at around 50C, though some go as low as 40C or as high as 60C. It is recommended to use a cooling fan with TPU.
Is printing TPU toxic?
Nope, printing TPU is not toxic. Because it is nontoxic, TPU also sees use in the biomedical field. It is, however, not food safe, as its isocyanates content can irritate the eyes, nose, and throat. TPU filament is relatively easy to use for 3D printing, especially when it comes to flexible materials.
Is TPU safe to breath?
Nope, it’s not safe to breath in anything that’s not air. If there’s enough oxygen in the air, inert gasses like neon or argon won’t do anything whatsoever. Helium is also fine. These gasses are used for breathing gasses (space suits, diving, etc). TPU is not safe to inhale regularly.
What is the best temp for PLA?
The best temperature will rely on the type of PLA you’re using and your 3D printer, but the range for PLA is around 210 ⁰C, but it also works well anywhere between 190 to 230 ⁰C depending on what you need. Your 3D prints should have great results as long as they don’t stray away from either direction. Do not forget to keep your cooling fans on while printing as the best results are produced with proper cooling.
Can anything be 3D printed?
The shortest answer is NO, you can’t print just anything. 3D printers will print almost every shape, object, or structure no matter how complex they may seem as it is done in fine layers and it constructs the object from the base. 3D printer constructing from the base There are different 3D printing filaments you can use but the most commonly used and available in standard diameters are the PC filament 1.75 and 2.85.
What temperature do you print nylon?
A temperature of 240 to 260 ⁰C is recommended when printing nylon with a bed temperature of around 70 to 100 ⁰C. You will also need a heating bed with nylon filament. Nylon can prove to be a challenge for first-time users but once you learn how to properly print using this material it becomes a powerful tool. Do not print with your cooling fans on as it needs to retain the temperature.
How is nylon heat resistant?
With low moisture absorption and high temperatures, nylons are ideal heat-resistant resins and the best if printing for durable parts. The nylon filaments need extruder temperatures of around 250 ⁰C, but some few brands will permit temperatures from as little as 200 ⁰C. 3D Printer Filament Manufacturers are increasingly improving their hardware and products, and with the PC 3D printer filament, it should be ideal for nylon as it is remarkably tough and heat resistant.
How fast can you print nylon?
The speeds at which you can print the nylon filament are higher compared to others, you can easily achieve speeds exceeding 70mm /s but when you 3D print the nylon filament above 70 mm /s it has less time for heating and you will have to adjust the nozzle to avoid under- extrusion. Printing using nylon might be a little difficult if you’ve never used it before but if you have the right tools you will produce outstanding results. A 3D Printer Filament Manufacturer will ensure you have the right tools to help you out.
Does PLA stick to nylon?
PLA will gladly stick to the nylon when 3D printing using adhesive methods such as glue stick, hair spray, or a blue painter’s tape. If you attempt to 3D print without a heated print surface the print may not come out as you had planned and will corrupt the print. Using the right bed surface when printing is crucial.
Is ABS toxic to print?
Yes, ABS might be toxic to your print but depending on the temperatures, if heated above 200 ⁰C in a 3D printer the fumes can be toxic which won’t be pleasant to some users as it discharges a strong smell when printing making it unbearable and toxic. But if used properly it will produce good results, it is also the second frequently used plastic in 3D. The emissions may vary 3 – 30 times when using ABS than when using PLA.
Does ABS need a cooling fan?
Cooling for ABS isn’t good for your print, especially when printing small objects. Your bed temperature should range from 100 ⁰C to 110⁰C, you might corrupt the print if ABS is cooled down hastily, this will cause it to shrink. As you can see in the image above, the top of the pyramid has an issue with extrusion temperature, it was printed at 210 ⁰C and with no cooling. Try experimenting with 220 ⁰C and you’ll get your accuracy.
Are carbon fiber filaments dangerous?
Yes, carbon fiber filaments can be a bit dangerous and you should use them with caution, they tend to be very abrasive, so you will have to buy a reinforced extruder or replace it after every few prints. For traditional printers, carbon fiber print is the best, it has proved to be one of the strongest you can use, they boost certain properties giving them an advantage over other traditional printers. You can find the carbon fiber filament from a 3D Printer Filament Manufacturer.
Are 3D printed parts strong?
3D printed parts are most certainly strong, strong enough that they are used in the making of common plastic materials that can endure a great sum of impact and also heat, it also depends on the material you’re using. In making some materials are made more powerful than others or durable, some materials can even be easily bent and compressed but this is achieved when using a TPU 3D printer filament, offering you unique possibilities. In 3D printing the final product should yield good results, it needs to be solid and not to forget durable. After you’ve bought your 3D printer, you will need to consider what type of filament you’re going to use which a 3D Printer Filament Manufacturer can guide you through. We hope the above information will be of use to you when you decide to purchase a 3D Printer of your own and what type of filament you’re going to use.
Conclusion
To wrap it up, 3D printer filaments are essential to our day to day activity. And the need for reliable 3D printer filaments in numerous industries made a lot of companies dive into the manufacturing and distribution 3D filaments.
However, not all 3D printer filament manufacturer can boast of sustained reputability and all-round efficiency for a long period of time. But surprisingly, this is one feat dreambot3D can boast of. We have been in the 3D printing industry for quite a while and understand all there is to know about 3D printing.
If you are in need of a highly proficient 3D printer filament manufacturer to cater to the day to day need of your production line, don’t hesitate to get in touch, we are just a call away.